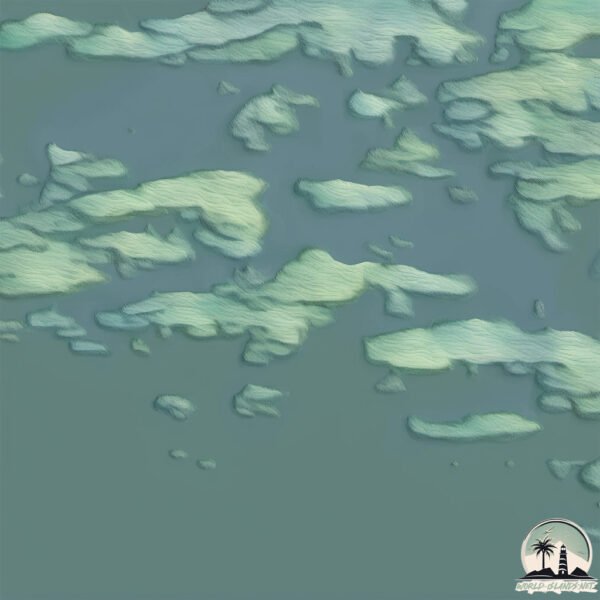
Welcome to Hector Island, a Polar island in the Hudson Strait, part of the majestic Arctic Ocean. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of what makes Hector Island unique – from its geography and climate to its population, infrastructure, and beyond. Dive into the details:
Geography and size of Hector Island
Size: 16.9 km²
Coastline: 51.4 km
Ocean: Arctic Ocean
Sea: Hudson Strait
Continent: North America
Hector Island is a Medium Island spanning 17 km² with a coastline of 51 km.
Archipel: Canadian Arctic Archipelago – A vast and remote region in northern Canada, consisting of a series of large and small islands known for their extreme Arctic environment and unique wildlife.
Tectonic Plate: North America – Covers North America and parts of the Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, characterized by diverse geological features and varying levels of seismic activity.
The geographic heart of the island is pinpointed at these coordinates:
Latitude: 63.63924739 / Longitude: -72.43455855
Climate and weather of Hector Island
Climate Zone: Polar
Climate Details: Tundra
Temperature: Cold
Climate Characteristics: The tundra climate features long, extremely cold winters and short, cool summers. Vegetation is limited to mosses, lichens, and small shrubs due to the low temperatures and short growing seasons. Biodiversity is low, but some specialized species thrive.
Topography and nature of Hector Island
Timezone: UTC-05:00
Timezone places: America/New_York
Max. Elevation: 114 m
Mean Elevation: 17 m
Vegetation: Herbaceous Cover
Tree Coverage: 28%
The mean elevation is 17 m. The highest elevation on the island reaches approximately 114 meters above sea level. The island is characterized by Plains: Flat, low-lying lands characterized by a maximum elevation of up to 200 meters. On islands, plains are typically coastal lowlands or central flat areas.
Dominating Vegetation: Herbaceous Cover
Comprising mainly of grasses, herbs, and ferns, these areas are common in prairies, meadows, and savannas, and can vary widely in species composition. Hector Island has a tree cover of 28 %.
Vegetation: 3 vegetation zones – Moderately Diverse Island
These islands start to show a broader range of ecological niches. With three vegetation zones, they may offer a mix of ecosystems like coastal areas, inland woods, and perhaps a distinct wetland or dry area. This diversity supports a wider range of flora and fauna, making these islands more ecologically complex than those with minimal diversity.
Infrastructure and Travelling to Hector Island
Does the island have a public airport? no.
There is no public and scheduled airport on Hector Island. The nearest airport is Kangiqsujuaq (Wakeham Bay) Airport, located 232 km away.
Does the island have a major port? no.
There are no major ports on Hector Island. The closest major port is PANGNIRTUNG, approximately 782 km away.
The mean population of Hector Island is 0 per km². Hector Island is Uninhabited. The island belongs to Canada.
Continuing your journey, Macdonald is the next notable island, situated merely km away.
Tiwi Island Hector simulation for EGU 2025
Simulation using the Unified Model Regional Nesting Suite at 1 km resolution with cloud water and cloud ice output on 90 vertical ...Tiwi Island Hector simulation for EGU 2025
Simulation using the Unified Model Regional Nesting Suite at 1 km ...
Simulation using the Unified Model Regional Nesting Suite at 1 km resolution with cloud water and cloud ice output on 90 vertical ...
Hector cloud
Hector Cloud is a unique meteorological phenomenon, a giant ...
Hector Cloud is a unique meteorological phenomenon, a giant thundercloud that regularly forms near the Tiwi Islands off the ...
Irene Hector, Island Harbour, Binfield, Newport
Isle of Wight UNESCO Biosphere Reserve Birthday message.
Isle of Wight UNESCO Biosphere Reserve Birthday message.
Mysterious Thundercloud: Meet Hector the Convector at 3 PM! #thunderclouds #hector
Heard about Hector, the mysterious thundercloud in Australia? Hector ...
Heard about Hector, the mysterious thundercloud in Australia? Hector shows up at 3 PM sharp, but Hector's not a person.
Storm Hector Hits the Island (14.06.2018)
HERE IS A SLO MO CLIP OF STORM HECTOR TAKEN YESTERDAY MORNING DOWN AT ...
HERE IS A SLO MO CLIP OF STORM HECTOR TAKEN YESTERDAY MORNING DOWN AT FENELLA BEACH IN PEEL.
Hector - A thunderstorm of the Tiwi islands | Australia
20191115.
20191115.
American Dad - General Hector Aldozar “The Dancer of Death” of Isla Island
American Dad Season 5 Episode 02 Moon Over Isla Island After the ...
American Dad Season 5 Episode 02 Moon Over Isla Island After the people of Isla Island overthrow General Juanito Pequeño, ...
"Hector the Convector: Australia’s Fascinating Daily Storm"
Hector the Convector is a well-known and remarkable thunderstorm that ...
Hector the Convector is a well-known and remarkable thunderstorm that forms almost daily over the Tiwi Islands in Australia's ...
Single Island Shores, Hector New York
Finger Lakes, Seneca Lake, Hector New York.
Finger Lakes, Seneca Lake, Hector New York.
Hector and Boskov try to survive on an island (Evil Con Carne/Grim & Evil)
Original episode: Grim & Evil: Season 2 Episode 11b: "Cod vs Hector" ...
Original episode: Grim & Evil: Season 2 Episode 11b: "Cod vs Hector" Credits to Maxwell Atoms and Cartoon Network Under ...
Hector the convector - Tiwi Islands - NT
Timelapse of Hector - one of more reliable thunderstorms on the planet.
Timelapse of Hector - one of more reliable thunderstorms on the planet.
Hector - The thundercloud that appears in Australia's island every afternoon
Island Boys speaking Spanish 🇨🇺 😈🦅🏝
Storm Hector at Rathlin Island
Storm Hector appeared the night before the 2018 St Kilda Challenge, a ...
Storm Hector appeared the night before the 2018 St Kilda Challenge, a race from Rathlin to St Kilda, about 200 NM. Wind speed ...
The Dark Island and Hector the Hero
演奏:タマバロックトリオ (ホイッスル)坪内達郎、棚沢正義 (ギター)きつねアキラ.
演奏:タマバロックトリオ (ホイッスル)坪内達郎、棚沢正義 (ギター)きつねアキラ.
Hector's dolphins between East Head (Okains Bay) and Pa Island
A bigger pod of hector's dolphins kept us company on and off for ...
A bigger pod of hector's dolphins kept us company on and off for around 30 mins on a group paddle during the Canterbury Sea ...
Hector Ó hEochagáin talks TG4 Travel Show 'Down Under' | Limerick Today
Gaeilgeoir and gallivanter Hector Ó hEochagáin joins Joe to chat about ...
Gaeilgeoir and gallivanter Hector Ó hEochagáin joins Joe to chat about his brand new TG4 travel series where he takes on ...
Hector Ana Fiesta Island Sunday June 10 2012 (go pro )
Me ansd Ana out for sunday bike ride in san diego.
Me ansd Ana out for sunday bike ride in san diego.
The Hector Cloud #shorts #short #mystery #viral #trending
Every year between September and March, a massive thundercloud named ...
Every year between September and March, a massive thundercloud named Hector, or "Hector the Convector," forms near ...
Yoshi's Island DS - Hector the Reflector Boss Fight
I was going to put a rhyme here, but then I remembered I'm not clever ...
I was going to put a rhyme here, but then I remembered I'm not clever enough to do that.
Ben Moves The Island | Lost S4.E14 #Shorts
Ben Moves The Island | Lost S4.E14 #Shorts.
Ben Moves The Island | Lost S4.E14 #Shorts.
Most Dangerous Island on Earth: Snake Island in Brazil #shorts #travel
Snake Island is the most dangerous island on Earth, according to CNN. ...
Snake Island is the most dangerous island on Earth, according to CNN. The island is located in the middle of the Amazon River ...
Island Touch's Hector "El Leon de la Bachata" and Liz performing during and ITDA social
Hector "El Leon" and Liz from Island Touch Debut a new and Original ...
Hector "El Leon" and Liz from Island Touch Debut a new and Original Bachata routine. Choreography: Hector Song: Falle by ...
Dead Island: Hector Lester & Lucy - Co Op Gameplay Part 10
Hector & Lucy seem to have a strange relationship. Lucy is obsessed ...
Hector & Lucy seem to have a strange relationship. Lucy is obsessed with blood and Hector wants to see our blood, whether it's ...
Hector Salamanca Doesn't Like The Island Boys #breakingbad
feedshorts #comedy #memes.
feedshorts #comedy #memes.
Canada is classified as Developed region: G7: Group of Seven – Major advanced economies, including Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The level of income is High income: OECD.
News – Latest Updates and Headlines from Hector Island
Stay informed with the most recent news and important headlines from Hector Island. Here’s a roundup of the latest developments.
Loading...
Please note: The data used here has been primarily extracted from satellite readings. Deviations from exact values may occur, particularly regarding the height of elevations and population density. Land area and coastline measurements refer to average values at mean high tide.