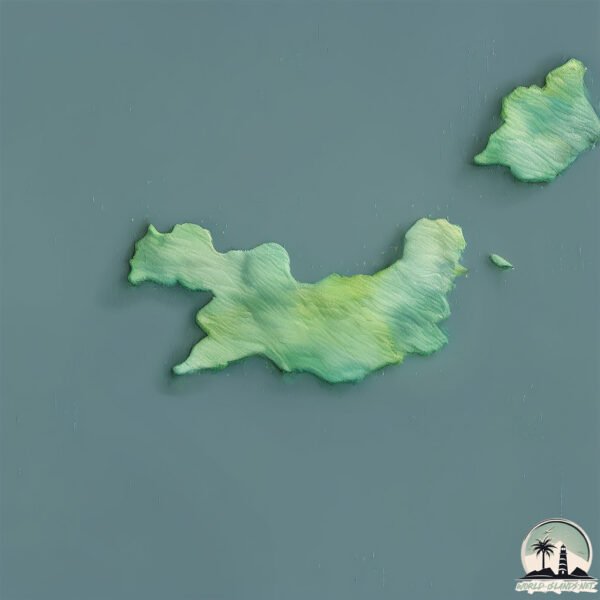
Welcome to Badger, a Temperate island in the Bass Strait, part of the majestic Pacific Ocean. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of what makes Badger unique – from its geography and climate to its population, infrastructure, and beyond. Dive into the details:
Geography and size of Badger
Size: 13.3 km²
Coastline: 32.3 km
Ocean: Pacific Ocean
Sea: Bass Strait
Continent: Oceania
Badger is a Medium Island spanning 13 km² with a coastline of 32 km.
Archipel: –
Tectonic Plate: Australia – A major tectonic plate covering Australia, New Zealand, and parts of the Indian and Pacific Oceans, known for its relative stability and occasional seismic activity.
The geographic heart of the island is pinpointed at these coordinates:
Latitude: -40.30903565 / Longitude: 147.87501343
Climate and weather of Badger
Climate Zone: Temperate
Climate Details: Temperate Oceanic Climate
Temperature: Warm Summer
Climate Characteristics: Known for its moderate year-round temperatures with ample rainfall and no dry season. Warm summers are characteristic.
Topography and nature of Badger
Timezone: UTC+10:00
Timezone places: Australia/Sydney
Max. Elevation: 17 m
Mean Elevation: 10 m
Vegetation: Open Woodland
Tree Coverage: 63%
The mean elevation is 10 m. The highest elevation on the island reaches approximately 17 meters above sea level. The island is characterized by Plains: Flat, low-lying lands characterized by a maximum elevation of up to 200 meters. On islands, plains are typically coastal lowlands or central flat areas.
Dominating Vegetation: Open Woodland
Characterized by sparsely distributed trees with open canopy allowing sunlight to penetrate, supporting grasses and shrubs underneath. Often found in drier or transitional environments. Badger has a tree cover of 63 %.
Vegetation: 5 vegetation zones – Highly Diverse Island
With five different vegetation zones, these islands offer a rich tapestry of ecosystems. The variety could include dense forests, open meadows, wetlands, coastal zones, and more. This level of diversity supports an intricate web of life, with each zone playing a vital role in the overall ecological health and balance of the island.
Infrastructure and Travelling to Badger
Does the island have a public airport? no.
There is no public and scheduled airport on Badger. The nearest airport is Flinders Island Airport, located 24 km away.
Does the island have a major port? no.
There are no major ports on Badger. The closest major port is PORT DALRYMPLE, approximately 144 km away.
The mean population of Badger is 0 per km². Badger is Uninhabited. The island belongs to Australia.
Continuing your journey, Prime Seal is the next notable island, situated merely km away.
Badger Island in Bass Strait
Famous Badger Island in Bass Strait. Home of the Stockhouse Brothers for more than 60 years. Beautiful Island surrounded by ...Badger Island in Bass Strait
Famous Badger Island in Bass Strait. Home of the Stockhouse Brothers ...
Famous Badger Island in Bass Strait. Home of the Stockhouse Brothers for more than 60 years. Beautiful Island surrounded by ...
Eventide, Badgers Island. Kittery, Maine
Memorial Bridge center span float-out from Badgers Island
February 08, 2012.
February 08, 2012.
Badger's Island From the Sky
Drone footage of Badger's Island in Danville, NH on Long Pond which is ...
Drone footage of Badger's Island in Danville, NH on Long Pond which is currently for sale for $84900. Call Better Homes and ...
Badger's Island Kittery Maine and Memorial Bridge
Badger's Island, Kittery Maine and the Memorial Bridge going to New ...
Badger's Island, Kittery Maine and the Memorial Bridge going to New Hampshire. An amazing sunset occurred while I was there ...
Monday, July 15th: Exploring Badgers Island
Food and views right across The Piscataqua Subscribe to WMUR on ...
Food and views right across The Piscataqua Subscribe to WMUR on YouTube now for more:
http://bit.ly/1lOjX9C Get more ...
Badger's Island Photos From the Sky
Still drone photos of Badger's Island on Long Pond in Danville, NH.
Still drone photos of Badger's Island on Long Pond in Danville, NH.
Badger Island, Chappell Group
Granny Smith visits Badger Island in the Chappell Isles, Furneaux ...
Granny Smith visits Badger Island in the Chappell Isles, Furneaux Group. Lovely beaches, good westerly shelter towards the sand ...
Kittery, Maine - Badger's Island Bridge
This is the bridge that goes to Kittery, ME.
This is the bridge that goes to Kittery, ME.
Explore the Beauty of Badger's Island: A Tranquil Oasis
Join us on a picturesque journey to Badger's Island, located on the ...
Join us on a picturesque journey to Badger's Island, located on the border of Maine and New Hampshire. Discover the stunning ...
23A Badgers Island in Kittery Maine | Jeff Mountjoy | Olde Port Properties
Multi-day time-lapse from Badger Island, Portsmouth, NH
Portmsouth New Hampshire Memorial Bridge time-lapse construction.
Portmsouth New Hampshire Memorial Bridge time-lapse construction.
server of weird superpowers
shoutout to swood for the bready fazbun model: ...
shoutout to swood for the bready fazbun model: ...
The Great Room Company builds on Badgers Island Maine
We designed & built this two unit condo on Badgers Island, Maine ...
We designed & built this two unit condo on Badgers Island, Maine overlooking the Piscataqua River and Portsmouth, New ...
Badger's Island - Adventures ahead
Spring is just around the corner and so is my 3 week trip to Svalbard. ...
Spring is just around the corner and so is my 3 week trip to Svalbard. I have started the usual preparations to this years badger ...
Badger's Quay & Pool's Island NL , Canada
Lobster Rolls & More from Buoy Shack on Badgers Island, Kittery ME
Not only does the Buoy Shack boast a beautiful waterfront location, it ...
Not only does the Buoy Shack boast a beautiful waterfront location, it also claims a special geographical distinction. As one of the ...
9 Badgers Island West #4 | MLS# 1130615 | Jeffrey Levine | Coldwell Banker Real Estate
Seacoast Real Estate Photography - Portsmouth.
Seacoast Real Estate Photography - Portsmouth.
Sailing Toward Badger Island - Tasmania
ACNH Blue Badger Island Tune
I couldn't find one online, so I made an island tune of "I Want to ...
I couldn't find one online, so I made an island tune of "I Want to Protect You", the Blue Badger's theme from Ace Attorney.
Inside 2 Little Badger Island, Moultonborough NH | Private Island on Lake Winnipesaukee! 🏝🔥
A Once-in-a-Lifetime Opportunity Has Just Hit the Market! Welcome to 2 ...
A Once-in-a-Lifetime Opportunity Has Just Hit the Market! Welcome to 2 Little Badger Island, a rare private island estate located in ...
Why Honey Badgers Might Be the Toughest Animals on Earth
Beth Shapiro explains to Joe Rogan why honey badgers are absolute ...
Beth Shapiro explains to Joe Rogan why honey badgers are absolute survival machines. From killing cobras to surviving lion ...
Kittery Propane Leak
Lt. Russ French describes what happened at Badger's Island West as it ...
Lt. Russ French describes what happened at Badger's Island West as it was closed and a “number of homes” were evacuated ...
1818 Badger's Island Cemetery, Kittery Maine
This is actually two separate "Cemeteries," the Willey Family ...
This is actually two separate "Cemeteries," the Willey Family Cemetery, and the William Badger Mausoleum. Location on Google ...
Australia is classified as Developed region: nonG7: Developed economies outside of the Group of Seven, characterized by high income and advanced economic structures. The level of income is High income: OECD.
News – Latest Updates and Headlines from Badger
Stay informed with the most recent news and important headlines from Badger. Here’s a roundup of the latest developments.
Loading...
Please note: The data used here has been primarily extracted from satellite readings. Deviations from exact values may occur, particularly regarding the height of elevations and population density. Land area and coastline measurements refer to average values at mean high tide.