Welcome to Cayo Iguana, a Tropical island in the North Atlantic Ocean, part of the majestic Atlantic Ocean. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of what makes Cayo Iguana unique – from its geography and climate to its population, infrastructure, and beyond. Dive into the details:
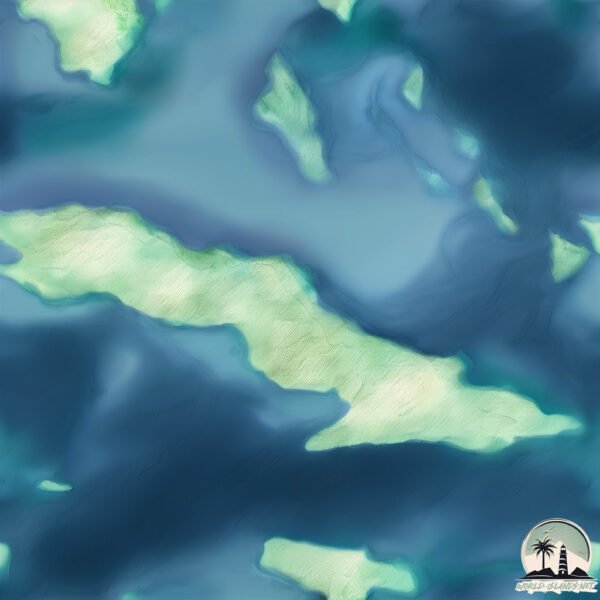
Geography and size of Cayo Iguana
Size: 5.32 km²
Coastline: 22.9 km
Ocean: Atlantic Ocean
Sea: North Atlantic Ocean
Continent: North America
Cayo Iguana is a Small Island spanning 5.3 km² with a coastline of 22.9 km.
Archipel: Greater Antilles – A major island group in the Caribbean, including Cuba, Jamaica, Hispaniola, and Puerto Rico, known for their rich history and diverse cultures.
Tectonic Plate: North America – Covers North America and parts of the Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, characterized by diverse geological features and varying levels of seismic activity.
The geographic heart of the island is pinpointed at these coordinates:
Latitude: 22.82765874 / Longitude: -79.55159367
Climate and weather of Cayo Iguana
Climate Zone: Tropical
Climate Details: Tropical Savanna, Wet
Temperature: Hot
Climate Characteristics: Defined by distinct wet and dry seasons with high temperatures year-round. Pronounced rainfall occurs during the wet season, while the dry season is marked by drought.
Topography and nature of Cayo Iguana
Timezone: UTC-05:00
Timezone places: America/New_York
Max. Elevation: 6 m
Mean Elevation: 3 m
Vegetation: Mangrove Forest
Tree Coverage: 77%
The mean elevation is 3 m. The highest elevation on the island reaches approximately 6 meters above sea level. The island is characterized by Plains: Flat, low-lying lands characterized by a maximum elevation of up to 200 meters. On islands, plains are typically coastal lowlands or central flat areas.
Dominating Vegetation: Mangrove Forest
Found in coastal areas and river deltas, these unique wetland ecosystems are adapted to saline conditions and are crucial for coastal protection and biodiversity. Cayo Iguana has a tree cover of 77 %.
Vegetation: 5 vegetation zones – Highly Diverse Island
With five different vegetation zones, these islands offer a rich tapestry of ecosystems. The variety could include dense forests, open meadows, wetlands, coastal zones, and more. This level of diversity supports an intricate web of life, with each zone playing a vital role in the overall ecological health and balance of the island.
Infrastructure and Travelling to Cayo Iguana
Does the island have a public airport? no.
There is no public and scheduled airport on Cayo Iguana. The nearest airport is Jardines Del Rey Airport, located 37 km away.
Does the island have a major port? no.
There are no major ports on Cayo Iguana. The closest major port is ISABELA DE SAGUA, approximately 6 km away.
The mean population of Cayo Iguana is 54 per km². Cayo Iguana is Gently Populated. The island belongs to Cuba.
The name of the island resonates across different cultures and languages. Here is how it is known around the world: Arabic: كوبا; German: Kuba; Spanish: Cuba; French: Cuba; Portuguese: Cuba; Russian: Куба; Chinese: 古巴岛
Continuing your journey, Cayo Santa Maria is the next notable island, situated merely km away.
Iguana Island -Cayo Iguana🤪one bit me #cayolargo #travel #nature #wildlife #caribbean #cuba #beach
Cayo Iguana is located in Cayo Largo del Sur, Cuba. Most of the people who visit this cay arrive there by boat and are those who ...Iguana Island -Cayo Iguana🤪one bit me #cayolargo #travel #nature #wildlife #caribbean #cuba #beach
Cayo Iguana is located in Cayo Largo del Sur, Cuba. Most of the people ...
Cayo Iguana is located in Cayo Largo del Sur, Cuba. Most of the people who visit this cay arrive there by boat and are those who ...
Cayo de las iguanas - exploring the island
The music used in this video is used with the permission of the ...
The music used in this video is used with the permission of the author: Pinacolada Banda - Recuerdo This video is about small ...
An island with dozens of iguanas! #travel #explore #iguana #iguanaisland #cuba #nature #wildlife
Swimming with Iguanas in Cayo Iguana 🦎🌊 | 🇨🇺🇨🇺 | #shorts #iguana #travelvlog #adventure
Discover the hidden gem of Cuba – Cayo Iguana! 🏝️ Known for its ...
Discover the hidden gem of Cuba – Cayo Iguana! 🏝️ Known for its turquoise waters, white sand beaches, and friendly wild ...
Tra le iguane a Cayo Iguana 🦎🏝️
Indovinate perchè questa isola si chiama Cayo Iguana? Cayo Iguana si ...
Indovinate perchè questa isola si chiama Cayo Iguana? Cayo Iguana si trova a Cayo Largo del Sur, a Cuba. Qui si incontrano ...
Cayo Largo Cuba, Iguana Island
A part of the "Super Reef" excursion on the CocoClub.
A part of the "Super Reef" excursion on the CocoClub.
Iguana Island, CAYO LARGO, Cuba #iguana #cayolargo #cuba
A place visited by many tourists is the Iguana Island, CAYO LARGO, ...
A place visited by many tourists is the Iguana Island, CAYO LARGO, Cuba. From what the boat captain said, this island was ...
SE2 - 45, Sailing Cuba! - Cayo Iguana
Season 2 - Episode 45 ... Sailing Cuba! After exploring the remote ...
Season 2 - Episode 45 ... Sailing Cuba! After exploring the remote Southern Cayos of La Jardines de la Reina for 3 weeks, we are ...
Cuba, Cayo Iguanas
Notre TOUR DU MONDE en VIDEO !! 1 minute pour vous faire voyager! ...
Notre TOUR DU MONDE en VIDEO !! 1 minute pour vous faire voyager! Vidéo #6: Cayo de las Iguanas!!! Escapade dans cette île, ...
Cayos en Cuba - Trinidad / Cayo Iguana
BaharyTravels te ofrece la oportunidad de llevarte a uno de los cayos ...
BaharyTravels te ofrece la oportunidad de llevarte a uno de los cayos más exóticos y desconocidos que hay en Cuba, Cayo ...
Views Around the World: Cayo Iguana, Cayo Largo, Cuba
Sit Back, Relax, And Enjoy! Maybe Take A Nap? IG: Adevnture.On.Earth.
Sit Back, Relax, And Enjoy! Maybe Take A Nap? IG: Adevnture.On.Earth.
Sailing Cuba, visiting Cayo Iguana
As we were sailing Cuba from Cienfuegos to Cayo del Rosario, we ...
As we were sailing Cuba from Cienfuegos to Cayo del Rosario, we dropped anchor at Cayo Iguana...
Super Reef Excursion – Cayo Largo, Cuba: Snorkeling, Iguanas, and Starfish [2023 ] *4K*
Check out our other videos in this CAYO LARGO series: *Starfish Cayo ...
Cayo Iguanas - Trinidad
BaharyTravels viaja hasta Trinidad para descubrir uno de sus ...
BaharyTravels viaja hasta Trinidad para descubrir uno de sus maravillosos Cayos, Cayo Iguanas & Blanco. Este video no es ...
IGUANA ISLAND Cayo Largo, Cuba
Une mère et ses deux fils partent à l'aventure en catamaran pour ...
Une mère et ses deux fils partent à l'aventure en catamaran pour explorer la mystérieuse île aux iguanes. ⛵ Entre navigation ...
Cayo Iguana Cuba
Sailing trip from Trinidad, Cuba to Cayo Iguana. on a 44' Catamaran ...
Sailing trip from Trinidad, Cuba to Cayo Iguana. on a 44' Catamaran under full sail. Topped out according to GPS at 24knotts.
Cayo Iguana Cuba
sailing trip out to Cayo Iguana Cuba.
sailing trip out to Cayo Iguana Cuba.
Cayo Largo Catamaran day trip
Full day catamaran trip, snorkeling, iguanas, lobster lunch, and more. ...
Full day catamaran trip, snorkeling, iguanas, lobster lunch, and more. Cayo Largo #cuba. Visited April 2023. 0:00 - marina 0:32 ...
ISLA IGUANA (ÎLE AUX IGUANES) - CAYO LARGO - CUBA
Île aux iguanes - Cayo Largo - Cuba Lors de l'excursion en catamaran, ...
Île aux iguanes - Cayo Largo - Cuba Lors de l'excursion en catamaran, nous faisons un arrêt à l'île aux iguanes (Isla Iguana).
Iguanas en Cayo Iguana (Cuba)
VISITING CAYO IGUANA ISLAND 🇨🇺🇨🇺🇨🇺 #shorts
Iguanas and a Cute Jutias on Iguanas Island, Cuba
Cayo Iguanas, Cuba.
Cayo Iguanas, Cuba.
Weltreise #92 - Trinidad, Cayo Iguana
Trinidad ist eine malerische Stadt im Herzen Kubas. Hier haben wir 4 ...
Trinidad ist eine malerische Stadt im Herzen Kubas. Hier haben wir 4 Tage verbracht und keinen davon bereut. Wir hatten einen ...
Cayo Macho Cayo Iguana CUBA 2016
Cayo Iguana un pequeño pedazo de paraíso tropical, se encuentra a unas ...
Cayo Iguana un pequeño pedazo de paraíso tropical, se encuentra a unas 20 millas de la costa de Trinidad, La excursión en ...
Catamaran Experience From Iberostar Ensenachos| Snorkeling, Dolphin Interaction & Iguana Island
Catamaran Experience at Cayo Santa Maria Cuba From Iberostar ...
Catamaran Experience at Cayo Santa Maria Cuba From Iberostar Ensenachos| Snorkeling| Dolphin Interaction and Iguana Island ...
Cuba is classified as Emerging region: G20: Group of Twenty – Major economies comprising both developed and emerging countries, representing the world’s largest economies. The level of income is Upper middle income.
News – Latest Updates and Headlines from Cayo Iguana
Stay informed with the most recent news and important headlines from Cayo Iguana. Here’s a roundup of the latest developments.
Loading...
Please note: The data used here has been primarily extracted from satellite readings. Deviations from exact values may occur, particularly regarding the height of elevations and population density. Land area and coastline measurements refer to average values at mean high tide.












![Super Reef Excursion – Cayo Largo, Cuba: Snorkeling, Iguanas, and Starfish [2023 ] *4K*](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/xtA7lcWY-cM/mqdefault.jpg)












