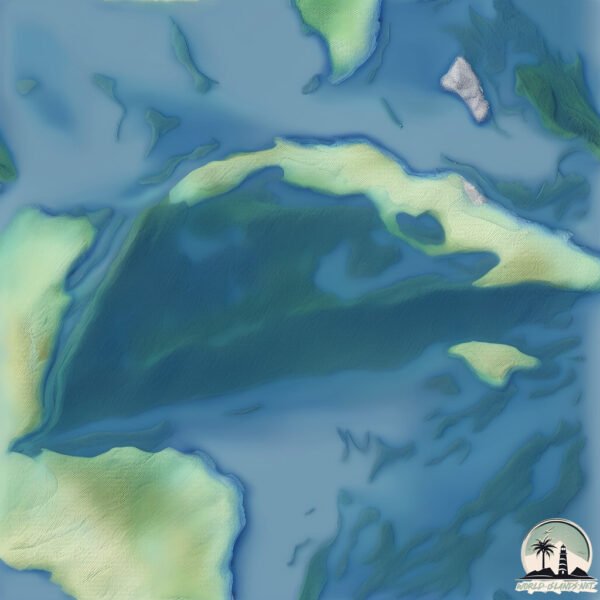
Welcome to Cayo Media Luna, a Tropical island in the Caribbean Sea, part of the majestic Atlantic Ocean. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of what makes Cayo Media Luna unique – from its geography and climate to its population, infrastructure, and beyond. Dive into the details:
Geography and size of Cayo Media Luna
Size: 56.5 km²
Coastline: 57.6 km
Ocean: Atlantic Ocean
Sea: Caribbean Sea
Continent: North America
Cayo Media Luna is a Medium Island spanning 57 km² with a coastline of 58 km.
Archipel: Greater Antilles – A major island group in the Caribbean, including Cuba, Jamaica, Hispaniola, and Puerto Rico, known for their rich history and diverse cultures.
Tectonic Plate: North America – Covers North America and parts of the Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, characterized by diverse geological features and varying levels of seismic activity.
The geographic heart of the island is pinpointed at these coordinates:
Latitude: 16.67295579 / Longitude: -85.49910638
Climate and weather of Cayo Media Luna
Climate Zone: Tropical
Climate Details: Tropical Rainforest Climate
Temperature: Hot
Climate Characteristics: This climate is typified by heavy rainfall throughout the year, high humidity, and consistently high temperatures, leading to lush rainforests and rich biodiversity. Seasonal temperature variations are minimal.
Topography and nature of Cayo Media Luna
Timezone: UTC-06:00
Timezone places: America/Chicago
Max. Elevation: 301 m
Mean Elevation: 81 m
Vegetation: Evergreen Broadleaf Forest
Tree Coverage: 72%
The mean elevation is 81 m. The highest elevation on the island reaches approximately 301 meters above sea level. The island is characterized by Hills: Gently sloping landforms with rounded tops, having a maximum elevation between 200 and 500 meters. Hills contribute to a varied landscape on islands.
Dominating Vegetation: Evergreen Broadleaf Forest
Characterized by dense, lush canopies of broadleaf trees that retain their leaves year-round. These forests are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions and are known for their high biodiversity. Cayo Media Luna has a tree cover of 72 %.
Vegetation: 11 vegetation zones – Exceptionally Diverse Island
Islands with more than ten vegetation zones are among the most ecologically rich and varied in the world. These islands are akin to miniature continents, boasting an incredible array of ecosystems. The sheer range of habitats, from high peaks to deep valleys, rainforests to deserts, creates a mosaic of life that is unparalleled. They are crucial for conservation and ecological studies.
Infrastructure and Travelling to Cayo Media Luna
Does the island have a public airport? yes.
Cayo Media Luna has a public and scheduled airport. The following airports are located on this island: La Laguna Airport.
Does the island have a major port? no.
There are no major ports on Cayo Media Luna. The closest major port is GUAYABAL, approximately 32 km away.
The mean population of Cayo Media Luna is 98 per km². Cayo Media Luna is Gently Populated. The island belongs to Honduras.
Continuing your journey, Cayo Guillermo is the next notable island, situated merely km away.
Exploring Cuba's Cayo Media Luna Island Paradise
Discover the intriguing history of Cayo Media Luna, also known as Half Moon Key! Join us as we explore how the island got its ...Exploring Cuba's Cayo Media Luna Island Paradise
Discover the intriguing history of Cayo Media Luna, also known as Half ...
Discover the intriguing history of Cayo Media Luna, also known as Half Moon Key! Join us as we explore how the island got its ...
Cayo Media Luna Island (from Cayo Guillermo Kempinski Resort)
Sailing from Cayo Guillermo Kempinski Resort (Cuba) to Cayo Media Luna ...
Sailing from Cayo Guillermo Kempinski Resort (Cuba) to Cayo Media Luna Island & snorkeling. The island has all you can eat ...
Cuba /Cayo Coco /Playa Pilar / Tropical island # Cayo Media Luna
Cayo Coco / White-sand ,coral reefs and lagoon.
Cayo Coco / White-sand ,coral reefs and lagoon.
Playa Pilar & Cayo Media Luna: Cayo Coco, Cuba
Embark on a visual journey to Playa Pilar Beach and Cayo Media Luna in ...
Embark on a visual journey to Playa Pilar Beach and Cayo Media Luna in Cuba! Join me as I explore the crystal-clear turquoise ...
Playa Luxury Cayo Guillermo - Cayo Media Luna, Cayo Guillermo, Cuba
As a guest at the Playa Luxury Cayo Guillermo you should take ...
As a guest at the Playa Luxury Cayo Guillermo you should take katamaran and go to Cayo Media Luna, a small islet located near ...
Media Luna Island really came through this year #couplegoals #tropical #boatlife
Crystal-clear waters, breathtaking ocean snorkeling, and a delicious ...
Crystal-clear waters, breathtaking ocean snorkeling, and a delicious lobster lunch ✨ An unforgettable experience you can book ...
Cuba Cayo Media Luna
Cayo Media Luna sortie en catamaran.
Cayo Media Luna sortie en catamaran.
20110118b Cayo Media Luna, Cuba
On the island of Cayo Media Luna, access by a shuttle boat from the ...
On the island of Cayo Media Luna, access by a shuttle boat from the Playa Pilar beach on the island of Cayo Guillermo. We did ...
Day trip to Cayo Media Luna - Day Number Three
Day trip to the Island - Cayo Media Luna Manguera Family Cuba 2025 Day ...
Day trip to the Island - Cayo Media Luna Manguera Family Cuba 2025 Day Number Three All White Theme February 2025 ...
Cayo Guillermo Excursion Media Luna visite guidée / Guided tour
Une visite guidée de l'île Media Luna qui se retrouve en face de la ...
Une visite guidée de l'île Media Luna qui se retrouve en face de la magnifique plage de Pilar à Cayo Guillermo, Cuba.
Playa Pilar, Cayo Guilermo, Cuba. ❤️ #beach #travel #cubabeach
Journey to Serenity: A Day at Cuba's Most Beautiful Beach
Embark on the ultimate adventure in Cayo Coco, Cuba with this ...
Embark on the ultimate adventure in Cayo Coco, Cuba with this must-watch video! Whether you're an early bird or a laidback ...
Unveiling Cayo Guillermo Cuba: Glass Bottom Boat Tour
Embark on an unforgettable journey through the crystal clear waters of ...
Embark on an unforgettable journey through the crystal clear waters of Cayo Coco, Cuba with a glass bottom boat tour! Witness ...
Snorkel @ Isla Medialuna (Barco Hundido)
Haciendo Snorkel en la Isla Medialuna - Playa Pilar - Cuba Julio 2011.
Haciendo Snorkel en la Isla Medialuna - Playa Pilar - Cuba Julio 2011.
Cayo Coco e Cayo Guilhermo Cuba Cayo Guilhermo, Praia Pilar e Ilha Media Luna 2ª Semana 1
Atualmente as ilhas de Cayo Coco e Cayo Guilhermo em Cuba estão ...
Atualmente as ilhas de Cayo Coco e Cayo Guilhermo em Cuba estão chamando cada vez mais atenção. Para quem gosta de se ...
Exploring Cuba's Paradise Aboard a Catamaran: Cayo Guillermo VLOG
Enjoy a full-day at sea aboard a catamaran with an open bar, stop for ...
Enjoy a full-day at sea aboard a catamaran with an open bar, stop for snorkeling at a coral reef, lunch included at the beautiful ...
MARAVILLOSA EXCURSIÓN Playa Pilar, snorkel e Isla Media Luna. CUBA
Si los videos anteriores te gustaron, este te SORPRENDERÁ POR SU BELLEZA.
Si los videos anteriores te gustaron, este te SORPRENDERÁ POR SU BELLEZA.
Media Luna Point Part 2
A second clip of the point near Media Luna with views of Cayo Afuera ...
A second clip of the point near Media Luna with views of Cayo Afuera and Cayo del Tierra.
Relax en Las Exumas, Playa Bahía Medialuna - Cayo Saddleback (2011)
A 60 Km de Nassau, después de un viaje de 50 minutos a 80 Km/h en un ...
A 60 Km de Nassau, después de un viaje de 50 minutos a 80 Km/h en un "powerboat" y con el culo molido por los saltos en el ...
Snorkel isla media luna
Snorkel y barco hundido isla media luna.
Snorkel y barco hundido isla media luna.
Discover the Hidden Gems of Cayo Coco, Cuba
Dive into the crystal clear waters of Cayo Coco, Cuba and explore the ...
Dive into the crystal clear waters of Cayo Coco, Cuba and explore the vibrant underwater world of the Caribbean Sea! Discover ...
ONE OF THE TOP BEACHES IN THE WORLD IS LOCATED IN CUBA!
Tag your beach buddy and add Playa Pilar in Cuba to your vacation ...
Tag your beach buddy and add Playa Pilar in Cuba to your vacation bucket list! You can get to this beach VIA a 3.5 hour flight from ...
Media Luna Resort & Spa (VF)
L'hôtel Media Luna Resort and Spa au Roatan est un complexe luxueux ...
L'hôtel Media Luna Resort and Spa au Roatan est un complexe luxueux situé face à la plage, sur la partie est de l'île et à environ ...
Honduras is classified as Emerging region: G20: Group of Twenty – Major economies comprising both developed and emerging countries, representing the world’s largest economies. The level of income is Upper middle income.
News – Latest Updates and Headlines from Cayo Media Luna
Stay informed with the most recent news and important headlines from Cayo Media Luna. Here’s a roundup of the latest developments.
Loading...
Please note: The data used here has been primarily extracted from satellite readings. Deviations from exact values may occur, particularly regarding the height of elevations and population density. Land area and coastline measurements refer to average values at mean high tide.