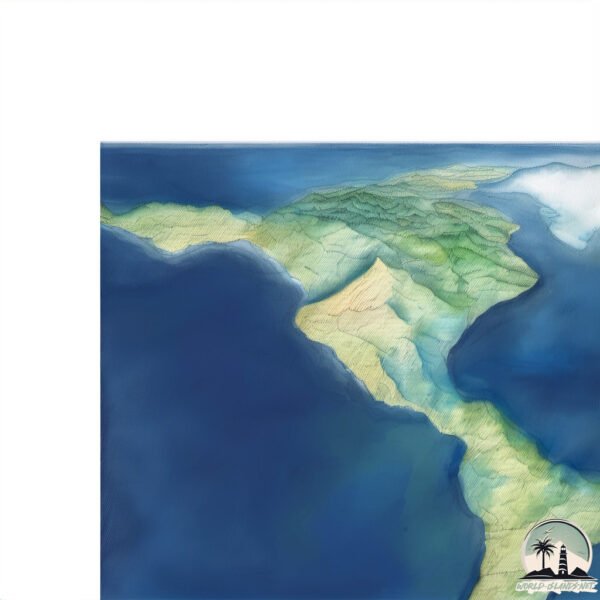
Welcome to Egg, a Continental island in the Gulf of Alaska, part of the majestic Pacific Ocean. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of what makes Egg unique – from its geography and climate to its population, infrastructure, and beyond. Dive into the details:
Geography and size of Egg
Size: 0.903 km²
Coastline: 7.4 km
Ocean: Pacific Ocean
Sea: Gulf of Alaska
Continent: North America
Egg is a Tiny Island spanning 0.903 km² with a coastline of 7.4 km.
Archipel: Aleutian Islands – A chain of islands stretching from Alaska to Russia, known for their rugged beauty, abundant wildlife, and volcanic activity.
Tectonic Plate: North America – Covers North America and parts of the Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, characterized by diverse geological features and varying levels of seismic activity.
The geographic heart of the island is pinpointed at these coordinates:
Latitude: 59.12919268 / Longitude: -144.44544634
Climate and weather of Egg
Climate Zone: Continental
Climate Details: Warm-Summer Humid Continental Climate
Temperature: Warm Summer
Climate Characteristics: Features warm summers and cold winters with consistent precipitation, common in higher latitudes.
Topography and nature of Egg
Timezone: UTC-09:00
Timezone places: America/Anchorage
Max. Elevation: 106 m
Mean Elevation: 18 m
Vegetation: Wetland
Tree Coverage: 63%
The mean elevation is 18 m. The highest elevation on the island reaches approximately 106 meters above sea level. The island is characterized by Plains: Flat, low-lying lands characterized by a maximum elevation of up to 200 meters. On islands, plains are typically coastal lowlands or central flat areas.
Dominating Vegetation: Wetland
These areas are saturated with water, either permanently or seasonally, and support aquatic plants. Wetlands are important for biodiversity and water filtration. Egg has a tree cover of 63 %.
Vegetation: 9 vegetation zones – Very Highly Diverse Island
Islands in this range are ecological powerhouses, showcasing a wide array of vegetation zones. Each zone, from lush rainforests to arid scrublands, coastal mangroves to mountainous regions, contributes to a complex and interdependent ecosystem. These islands are often hotspots of biodiversity, supporting numerous species and intricate ecological processes.
Infrastructure and Travelling to Egg
Does the island have a public airport? no.
There is no public and scheduled airport on Egg. The nearest airport is Egegik Airport, located 9 km away.
Does the island have a major port? no.
There are no major ports on Egg. The closest major port is EGEGIK, approximately 8 km away.
The mean population of Egg is 0 per km². Egg is Uninhabited. The island belongs to United States of America.
Continuing your journey, Little St Simons is the next notable island, situated merely km away.
The Isle of Eigg
Just off Scotland, a tiny island with one main road is a testament to human independence. Kroft reported from Eigg in 2017.The Isle of Eigg
Just off Scotland, a tiny island with one main road is a testament to ...
Just off Scotland, a tiny island with one main road is a testament to human independence. Kroft reported from Eigg in 2017.
Earth from Space: Egg Island
Earth from Space is presented by Kelsea Brennan-Wessels from the ESA ...
Earth from Space is presented by Kelsea Brennan-Wessels from the ESA Web TV virtual studios. Since it's Easter, let's have a ...
Egg Island, Eleuthera, Bahamas
Interesting Islands | 60 Minutes Full Episodes
From 2017, Steve Kroft's visit to the Isle of Eigg, a unique island ...
From 2017, Steve Kroft's visit to the Isle of Eigg, a unique island off the coast of Scotland. From 2019, Anderson Cooper's story on ...
Horn shark egg spotted in California with a tiny, moving embryo inside
Did you know that baby sharks hatch from these strangely shaped eggs? ...
Did you know that baby sharks hatch from these strangely shaped eggs? A beachcomber's video of a horn shark egg that had ...
GREEN EGG ISLAND HIKE HONG KONG | HOW TO HIKE GREEN EGG ISLAND(How to get there, views, highlights)
Hong Kong's GREEN EGG ISLAND is off the coast of Clearwater Bay area ...
Hong Kong's GREEN EGG ISLAND is off the coast of Clearwater Bay area in Sai kung. You can walk across chest-deep water to ...
Green Egg Island: an unusual oasis in Hong Kong
The Green Egg Island is near Clear Water Bay in Sai Kung, Hong Kong. ...
The Green Egg Island is near Clear Water Bay in Sai Kung, Hong Kong. It looks like a fried egg with a green yolk, hence it is ...
Go Diego Go Egg Island
Dora Diego Alicia and Baby Jaguar to visit The Dinosaur Musuem of ...
Dora Diego Alicia and Baby Jaguar to visit The Dinosaur Musuem of National History.
Man Steals T-Rex Dinosaur EGG | Jurassic World Water Dinosaurs Hunt #dinosaur #dinosaurvideo
Tourist staying in Jurassic park resort steal Dinosaur Egg. ...
Tourist staying in Jurassic park resort steal Dinosaur Egg. Tyrannosaurus Rex Dinosaurs smells its Egg and goes to save the ...
Green egg island / How to get the / easy hike with beautiful view #exploremore
How to get there? Diamond hill mtr station exit c2 get a bus no. 91 ...
How to get there? Diamond hill mtr station exit c2 get a bus no. 91 clearwater bay get off at tai au mun to get the easiest way turn ...
How to Turn One Egg into a Michelin-Star Dessert | "Floating Islands" | Food Wishes
These floating islands with vanilla crème Anglaise are a spectacular, ...
These floating islands with vanilla crème Anglaise are a spectacular, Michelin-star-level dessert, and all you need to pull off this ...
The One piece World attack on egg Island everyone its over for them #onepiece #anime #luffy #robin
#7: Atlantis - The Edfu Texts & The Island of the Egg
Apocalypse Episode 7: This episode presents a possible link between ...
Apocalypse Episode 7: This episode presents a possible link between Atlantis and The Island of the Egg story found in the Edfu ...
Dying for Eggs!! Papua’s Dangerous Island Food!!
Thanks to BetterHelp for sponsoring this video! Visit ...
Egg Island Advertisment V2
school p[roejct.
school p[roejct.
Why is it called egg island? Guess we'll never know 🥚🏝️
sailingfamily #travel #boatlife #shorts #bahamas #caribbean.
sailingfamily #travel #boatlife #shorts #bahamas #caribbean.
Egg Island Cave Entrance Location Point Of No Return Ghost Recon Breakpoint
This video shows where to find cave entrance on Egg Island Point Of No ...
This video shows where to find cave entrance on Egg Island Point Of No Return Mission Ghost Recon Breakpoint. You need to ...
One Piece Egghead Island Opening Secrets
Egg Head is about to hit SO HARD. One Piece is at its peak saga for ...
Egg Head is about to hit SO HARD. One Piece is at its peak saga for real. Hit the sub and check me out below if you like what you ......[+] Show More EGG ISLAND - Faranoid
EGG ISLAND 의 데뷔 앨범 " EGG " 첫번째 타이틀곡 "Faranoid" 뮤직비디오를 공개 합니다 비트 커버 출처: ...
EGG ISLAND 의 데뷔 앨범 " EGG " 첫번째 타이틀곡 "Faranoid" 뮤직비디오를 공개 합니다 비트 커버 출처: ...
EGG ISLET 🥚 (My Singing Monsters)
just testing out Fl Studio... don't ask questions... PROGRAMS I USE: ✓ ...
just testing out Fl Studio... don't ask questions... PROGRAMS I USE: ✓ Blender 2.7 ✓ Moho ✓ Audacity ✓ GarageBand ...
Exploring Green Egg Island (綠蛋島) in Clear Water Bay (4K Drone Video)
There are so many hidden paradise in Hong Kong and Green Egg Island in ...
There are so many hidden paradise in Hong Kong and Green Egg Island in Clear Water Bay is one of them. This island can be ...
My Singing Monsters - Wublin Island - All Eggs Fan Made! MSM 4k
Wublin Island - All Eggs Fan Made - My Singing Monsters MSM ...
Wublin Island - All Eggs Fan Made - My Singing Monsters MSM TIMESTAMPS: 0:00 - Brump 0:07 - Zynth 0:28 - Poewk 0:36 ...
The Final Journey of One Piece Begins! 🌊⚔️From Egghead to the Final War…
The Final Journey of One Piece Begins! ⚔️ From Egghead to the Final ...
The Final Journey of One Piece Begins! ⚔️ From Egghead to the Final War… every arc brings us closer to the truth of the One ...
Broke A Giant Lizard's Egg | Journey 2 The Mysterious Island | #movie #film
CineMatic Moments Presents: Broke A Giant Lizard's Egg Catch this ...
CineMatic Moments Presents: Broke A Giant Lizard's Egg Catch this quick highlight from Journey 2 The Mysterious Island 2012 ...
First Easter Egg In Dead Island 2 and its Sad!
cars #easteregg #disney #deadisland2 subnautica gameplay,subnautica ...
cars #easteregg #disney #deadisland2 subnautica gameplay,subnautica 3,subnautica mods,subnautica news,subnautica ...
United States of America is classified as Developed region: G7: Group of Seven – Major advanced economies, including Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The level of income is High income: OECD.
News – Latest Updates and Headlines from Egg
Stay informed with the most recent news and important headlines from Egg. Here’s a roundup of the latest developments.
Loading...
Please note: The data used here has been primarily extracted from satellite readings. Deviations from exact values may occur, particularly regarding the height of elevations and population density. Land area and coastline measurements refer to average values at mean high tide.