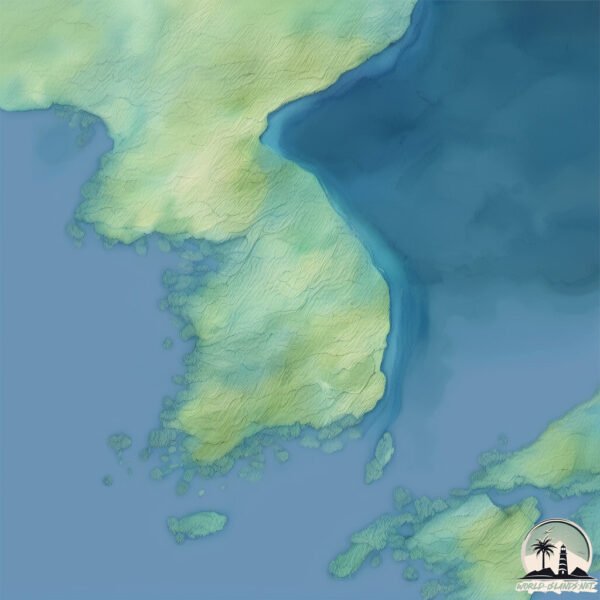
Welcome to Kuk-to, a Temperate island in the Japan Sea, part of the majestic Pacific Ocean. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of what makes Kuk-to unique – from its geography and climate to its population, infrastructure, and beyond. Dive into the details:
Geography and size of Kuk-to
Size: 0.696 km²
Coastline: 4 km
Ocean: Pacific Ocean
Sea: Japan Sea
Continent: Asia
Kuk-to is a Tiny Island spanning 0.696 km² with a coastline of 4 km.
Archipel: –
Tectonic Plate: Amur – A minor tectonic plate in the region of the Amur River at the border of Russia and China, involved in complex interactions with the Pacific and Eurasian plates.
The geographic heart of the island is pinpointed at these coordinates:
Latitude: 34.79818992 / Longitude: 128.40211717
Climate and weather of Kuk-to
Climate Zone: Temperate
Climate Details: Humid Subtropical Climate
Temperature: Hot Summer
Climate Characteristics: With continuous rainfall and hot summers, this climate is common in some coastal regions, supporting diverse vegetation.
Topography and nature of Kuk-to
Timezone: UTC+09:00
Timezone places: Asia/Tokyo
Max. Elevation: 53 m
Mean Elevation: 38 m
Vegetation: Open Woodland
Tree Coverage: 34%
The mean elevation is 38 m. The highest elevation on the island reaches approximately 53 meters above sea level. The island is characterized by Plains: Flat, low-lying lands characterized by a maximum elevation of up to 200 meters. On islands, plains are typically coastal lowlands or central flat areas.
Dominating Vegetation: Open Woodland
Characterized by sparsely distributed trees with open canopy allowing sunlight to penetrate, supporting grasses and shrubs underneath. Often found in drier or transitional environments. Kuk-to has a tree cover of 34 %.
Vegetation: 2 vegetation zones – Low Diversity Island
Islands with two distinct vegetation zones offer slightly more ecological variety. These zones could be due to differences in elevation, moisture, or other environmental factors. While still limited in biodiversity, these islands may offer a contrast between the two zones, such as a coastline with mangroves and an inland area with grassland.
Infrastructure and Travelling to Kuk-to
Does the island have a public airport? no.
There is no public and scheduled airport on Kuk-to. The nearest airport is Wonsan Kalma International Airport, located 26 km away.
Does the island have a major port? no.
There are no major ports on Kuk-to. The closest major port is WONSAN, approximately 30 km away.
The mean population of Kuk-to is 508 per km². Kuk-to is Densely Populated. The island belongs to South Korea.
Continuing your journey, Yokchi-do is the next notable island, situated merely km away.
😲Can you believe this is real?! 3 Cook Islands dollars 💵🧜♀️🦈 #rarotonga #cookislands #Polynesia
😲Can you believe this is real?! 3 Cook Islands dollars 💵🧜♀️🦈 #rarotonga #cookislands #Polynesia
My favorite Island in Thailand🌿 - Koh Kood 🫶🏼 #thailand #travel #kohkood #island #paradise
Cook Islands Vacation Travel Guide | Expedia
The Cook Islands – The land of pristine white sands fringed by coconut ...
The Cook Islands – The land of pristine white sands fringed by coconut palms. Experience the castaway island magic as you ...
FestPAC 2024 feat. Cook Islands Ladies’ Cultural Dance | Capitol Modern, Honolulu, Oahu, Hawaii, USA
pacificisland #pacificislandmusic #cookislands #culturaldance ...
pacificisland #pacificislandmusic #cookislands #culturaldance #islandlife #polynesianculture #polynesia #polynesian ...
Cook Islands 🇨🇰 to Singapore 🇸🇬
Phu Quoc Island VIETNAM Itinerary MISTAKES to Avoid
Phu Quoc Island VIETNAM Itinerary MISTAKES to Avoid #shorts ...
Phu Quoc Island VIETNAM Itinerary MISTAKES to Avoid #shorts #phuquocisland #vietnam #travel #trending #trendingshorts ...
The most underrated island in Thailand | Koh Chang Island
Negara terkecil di dunia. Cook Island #shorts #feedshorts
Cook Islands Visa fee for Pakistani. #cookislands #cookislandstourism #CookIslandsToTheWorld
Koh Kood: Discover Thailand’s Hidden Island Paradise! #travelgram #bucketlisttravel #thailand
Experience the untouched beauty of Koh Kood, Thailand's hidden ...
Experience the untouched beauty of Koh Kood, Thailand's hidden tropical paradise! From stunning beaches like Ao Tapao to ...
10 THINGS TO DO IN MONTENEGRO #montenegrotravel #kotor #uktravelblogger
5 DAY MONTENEGRO ITINERARY ⬇️ Day 1 – Kotor Old Town Walk the city ...
5 DAY MONTENEGRO ITINERARY ⬇️ Day 1 – Kotor Old Town Walk the city walls & fortress ⛪ St. Tryphon Cathedral ...
This Couple 😭❤️ Lee Si-an and Yuk Jun-seo Singles Inferno S4 Korean Dating Show #shorts
LETS REACH 100 LIKES! Can we get 100K subscribers? singles inferno ...
LETS REACH 100 LIKES! Can we get 100K subscribers? singles inferno season 4 korean dating show reality episode 7 8 ...
About the Cook Islands
Two young boys tell you their story about the Cook Islands.
Two young boys tell you their story about the Cook Islands.
Ko Kai (Chicken Island), Krabi, Thailand. #kokai #krabi #thailand #travelshorts #internationaltrip
Welcome to Ko Kai (Chicken Island) 🏝️! Discover this stunning Thai ...
Welcome to Ko Kai (Chicken Island) 🏝️! Discover this stunning Thai island with crystal-clear waters, amazing beaches, and the ...
The Tragic End of Captain Cook: The Clash of Two Cultures
Join us as we unravel the complex story of Captain Cook's fatal ...
Join us as we unravel the complex story of Captain Cook's fatal encounter with the Hawaiian people. Misunderstandings ...
Endgame couple❤️🔥🔥 Single's Inferno S4 Netflix Korean dating show Lee Sian x Yuk Junseo
Top 5 places to visit in New Zealand
Escape to the Spectacular Landscapes of New Zealand! 🏔️ Immerse ...
Escape to the Spectacular Landscapes of New Zealand! 🏔️ Immerse yourself in the breathtaking beauty of Milford Sound, ...
Rarotonga Cook Islands 🛫 Takeoff | #TakeOff #WindowSeat
Takeoff of JQ 112 in RAR Rarotonga, Cook Islands at 9am. Tail number: ...
Takeoff of JQ 112 in RAR Rarotonga, Cook Islands at 9am. Tail number: VH-OYT Seat: 22F #Takeoffandlanding #Rarotonga ...
Battle for kuk island Comparison
Credit goes to shinigami and jabmoreno *NO COPYRIGHT INFRINGEMENT ...
Credit goes to shinigami and jabmoreno *NO COPYRIGHT INFRINGEMENT INTENDED* Disclaimer: All material belongs to their ...
THIS IS THE SHOEBILL STORK! #shorts #shoebillstork #youtubeshorts
Subscribe to my channel for more! 🙂 Meet Sushi, the Shoebill Stork, ...
Subscribe to my channel for more! 🙂 Meet Sushi, the Shoebill Stork, otherwise known as Balaeniceps rex. The shoebill stork is an ...
PNG Kumuls vs Cook Island Aitu Pacific Championships 3rd Nov 2024 kickoff #rugbyleague #nrl
Date: 3rd November 2024 PNG Kumuls vs Cook Island Aitu Pacific ...
Date: 3rd November 2024 PNG Kumuls vs Cook Island Aitu Pacific Championships 3rd Nov 2024 kickoff #rugbyleague #nrl.
PNG Kumuls Debut Cooper Bai and Finley Glare 🇵🇬🥳 #pngkumuls #pngvscookisland #png #nrl #rugbyleague
How to Make Grilled Octopus
RIP Dr. Octopus #shorts Hit me up on TikTok for different and more ...
South Korea is classified as Emerging region: MIKT: Mexico, Indonesia, South Korea, and Turkey – Economies recognized for their development potential and emerging market status. The level of income is High income: OECD.
News – Latest Updates and Headlines from Kuk-to
Stay informed with the most recent news and important headlines from Kuk-to. Here’s a roundup of the latest developments.
Loading...
Please note: The data used here has been primarily extracted from satellite readings. Deviations from exact values may occur, particularly regarding the height of elevations and population density. Land area and coastline measurements refer to average values at mean high tide.