Langon
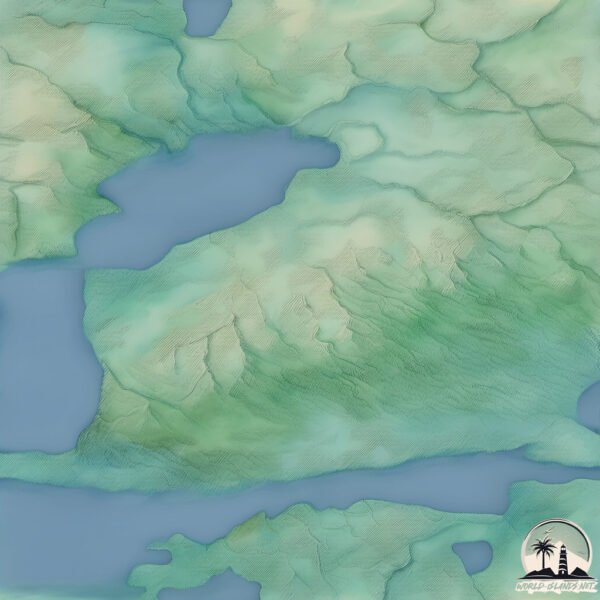
Welcome to Langon, a Continental island in the Gulf of Bothnia, part of the majestic Atlantic Ocean. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of what makes Langon unique – from its geography and climate to its population, infrastructure, and beyond. Dive into the details:
- Geography and Size: Explore the island’s size and location.
- Climate and Weather: Weather patterns and temperature.
- Topography and Nature: Uncover the natural wonders of the island.
- Infrastructure and Travelling: Insights on reaching, staying, and making the most of your visit.
- News and Headlines: Latest News.
Geography and size of Langon
Size: 1.397 km²
Coastline: 7.3 km
Ocean: Atlantic Ocean
Sea: Gulf of Bothnia
Continent: Europe
Langon is a Small Island spanning 1.4 km² with a coastline of 7.3 km.
Archipel: –
Tectonic Plate: Eurasia – One of the world’s largest tectonic plates, the Eurasian Plate covers a significant portion of Europe and Asia. It’s characterized by diverse geological features, including the Ural Mountains, the European Plain, and the Himalayas formed from its collision with the Indian Plate.
The geographic heart of the island is pinpointed at these coordinates:
Latitude: 64.68748598 / Longitude: 23.23839307
Climate and weather of Langon
Climate Zone: Continental
Climate Details: Subarctic Climate
Temperature: Cold Summer
Climate Characteristics: Characterized by long, extremely cold winters and short, cool summers, often found in northern latitudes of North America and Eurasia.
Topography and nature of Langon
Timezone: UTC+02:00
Timezone places: Europe/Helsinki
Max. Elevation: 50 m
Mean Elevation: 32 m
Vegetation: Evergreen Needleleaf Forest
Tree Coverage: 80%
The mean elevation is 32 m. The highest elevation on the island reaches approximately 50 meters above sea level. The island is characterized by Plains: Flat, low-lying lands characterized by a maximum elevation of up to 200 meters. On islands, plains are typically coastal lowlands or central flat areas.
Dominating Vegetation: Evergreen Needleleaf Forest
Dominated by evergreen coniferous trees such as pines and firs, which retain their needle-like leaves throughout the year. These forests are often found in cooler climates. Langon has a tree cover of 80 %.
Vegetation: 5 vegetation zones – Highly Diverse Island
With five different vegetation zones, these islands offer a rich tapestry of ecosystems. The variety could include dense forests, open meadows, wetlands, coastal zones, and more. This level of diversity supports an intricate web of life, with each zone playing a vital role in the overall ecological health and balance of the island.
Infrastructure and Travelling to Langon
Does the island have a public airport? no.
There is no public and scheduled airport on Langon. The nearest airport is Luleå Airport, located 47 km away.
Does the island have a major port? no.
There are no major ports on Langon. The closest major port is KOTKA, approximately 36 km away.
The mean population of Langon is 26 per km². Langon is Gently Populated. The island belongs to Finland.
Continuing your journey, Stora Brandon is the next notable island, situated merely km away.
David Gilmour - On An Island feat. Crosby & Nash (Remember That Night)



Finland is classified as Developed region: nonG7: Developed economies outside of the Group of Seven, characterized by high income and advanced economic structures. The level of income is High income: OECD.
News – Latest Updates and Headlines from Langon
Stay informed with the most recent news and important headlines from Langon. Here’s a roundup of the latest developments.
Please note: The data used here has been primarily extracted from satellite readings. Deviations from exact values may occur, particularly regarding the height of elevations and population density. Land area and coastline measurements refer to average values at mean high tide.
