New Guinea
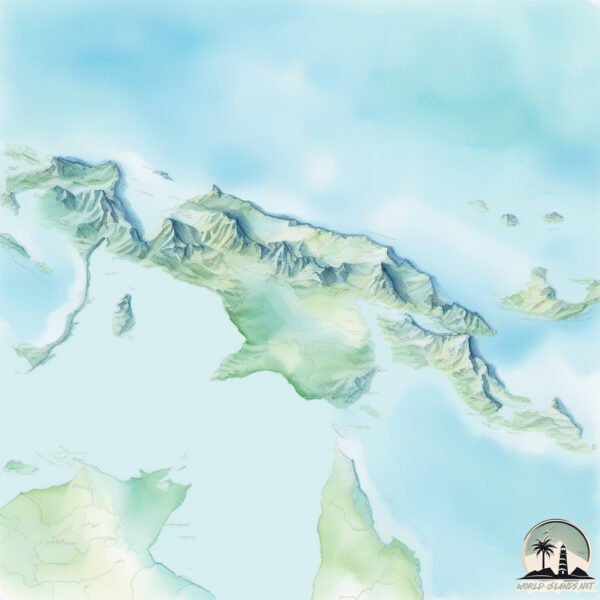
Welcome to New Guinea, a Tropical island in the Arafura Sea, part of the majestic Pacific Ocean. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of what makes New Guinea unique – from its geography and climate to its population, infrastructure, and beyond. Dive into the details:
- Geography and Size: Explore the island’s size and location.
- Climate and Weather: Weather patterns and temperature.
- Topography and Nature: Uncover the natural wonders of the island.
- Infrastructure and Travelling: Insights on reaching, staying, and making the most of your visit.
- News and Headlines: Latest News.
Geography and size of New Guinea
Size: 773751 km²
Coastline: 33430 km
Ocean: Pacific Ocean
Sea: Arafura Sea
Continent: Oceania
New Guinea is a Colossal Island spanning 773751 km² with a coastline of 33430 km.
Archipel: Melanesia – A subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, including countries like Fiji, Solomon Islands, and Vanuatu, known for their diverse cultures and languages.
Tectonic Plate: Australia – A major tectonic plate covering Australia, New Zealand, and parts of the Indian and Pacific Oceans, known for its relative stability and occasional seismic activity.
The geographic heart of the island is pinpointed at these coordinates:
Latitude: -5.33161786 / Longitude: 140.94463967
Climate and weather of New Guinea
Climate Zone: Tropical
Climate Details: Tropical Rainforest Climate
Temperature: Hot
Climate Characteristics: This climate is typified by heavy rainfall throughout the year, high humidity, and consistently high temperatures, leading to lush rainforests and rich biodiversity. Seasonal temperature variations are minimal.
Topography and nature of New Guinea
Timezone: UTC+10:00
Timezone places: Australia/Sydney
Max. Elevation: 4884 m Puncak Jaya
Mean Elevation: 588 m
Vegetation: Evergreen Broadleaf Forest
Tree Coverage: 69%
The mean elevation is 588 m. Dominating the island’s landscape, the majestic “Puncak Jaya” rises as the highest peak, soaring to impressive heights. The island is characterized by Mountains: High, steeply elevated landforms. Characterized by both a high maximum elevation (over 500 meters) and a high mean elevation, creating rugged, mountainous terrains on islands.
Dominating Vegetation: Evergreen Broadleaf Forest
Characterized by dense, lush canopies of broadleaf trees that retain their leaves year-round. These forests are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions and are known for their high biodiversity. New Guinea has a tree cover of 69 %.
Vegetation: 18 vegetation zones – Exceptionally Diverse Island
Islands with more than ten vegetation zones are among the most ecologically rich and varied in the world. These islands are akin to miniature continents, boasting an incredible array of ecosystems. The sheer range of habitats, from high peaks to deep valleys, rainforests to deserts, creates a mosaic of life that is unparalleled. They are crucial for conservation and ecological studies.
Infrastructure and Travelling to New Guinea
Does the island have a public airport? yes.
New Guinea has a public and scheduled airport. The following airports are located on this island: Aitape Airport, Chimbu Airport, Goroka Airport, Gurney Airport, Girua Airport, Kiunga Airport, Kikori Airport, Kerema Airport, Madang Airport, Mount Hagen Kagamuga Airport, Mendi Airport, Moro Airport, Nadzab Airport, Port Moresby Jacksons International Airport, Tari Airport, Tabubil Airport, Tapini Airport, Vanimo Airport, Wapenamanda Airport, Wewak International Airport, Woitape Airport, Yasuru Airport, Bosset Airport, Nop Goliat Dekai Airport, Okpahik Airstrip, Diphikin Airstrip, Iwur Airstrip, Kiwi Airstrip, Oklip Airstrip, Okyap Airstrip, Sape Airstrip, Sumtamon Airstrip, Yapil Airstrip, Awimbon Airstrip, Kubibkop Airport, Molding Airstrip, Tarup Airstrip, Tinibil Airstrip, Okbab Airstrip, Alemson Airstrip, Kotyobakon Airstrip, Mipol Airstrip, Binban Airstrip, Kaklup Airstrip, Maksum Airstrip, Pedam Airstrip, Dumpasik Airstrip, Bordamban Airport, Kirimu Airstrip, Hangmata Airstrip, Bilogai-Sugapa Airport, Tadji Airport, Awaba Airport, Ihu Airport, Kokoda Airport, Kamusi Airport, Lake Murray Airport, Obo Airport, Balimo Airport, Suki Airport, Tufi Airport, Nuku Airport, Baimuru Airport, Wipim Airport, Sasereme Airport, Nabire Airport, Mozes Kilangin Airport, Bokondini Airport, Dortheys Hiyo Eluay International Airport, Kiwirok Airstrip, Oksibil Airport, Senggeh Airport, Werur Airport, Mopah International Airport, Tanah Merah Airport, Fakfak Airport, Kaimana Airport, Rendani Airport, Wamena Airport, Domine Eduard Osok Airport.
Does the island have a major port? yes.
New Guinea is home to a major port. The following ports are situated on the island: MANOKWARI ROAD, AMAMAPARE, MERAUKE, DISCOVERY BAY, ORO BAY, LAE, VANIMO, JAYAPURA.
The mean population of New Guinea is 20 per km². New Guinea is Gently Populated. The island belongs to Papua New Guinea.
The name of the island resonates across different cultures and languages. Here is how it is known around the world: Arabic: غينيا الجديدة; German: Neuguinea; Spanish: Nueva Guinea; French: Nouvelle-Guinée; Portuguese: Nova Guiné; Russian: Новая Гвинея; Chinese: 新幾內亞
Continuing your journey, Mam Dadi is the next notable island, situated merely km away.
The Skeleton Tribe of Papua New Guinea lives in the heart of the Chimbu region not too far from Moun



Papua New Guinea is classified as Developing region: Regions characterized by lower income levels, with economies in the process of industrialization and modernization. The level of income is Lower middle income.
News – Latest Updates and Headlines from New Guinea
Stay informed with the most recent news and important headlines from New Guinea. Here’s a roundup of the latest developments.
Social Media Posts about New Guinea
Please note: The data used here has been primarily extracted from satellite readings. Deviations from exact values may occur, particularly regarding the height of elevations and population density. Land area and coastline measurements refer to average values at mean high tide.
