Newfoundland
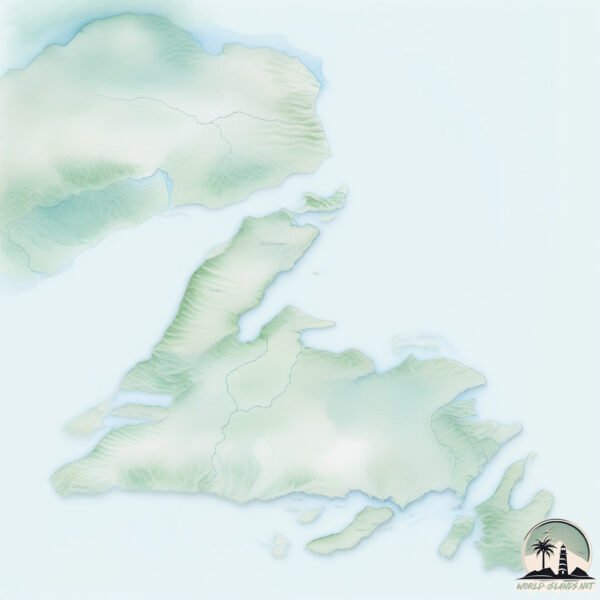
Welcome to Newfoundland, a Continental island in the Labrador Sea, part of the majestic Atlantic Ocean. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of what makes Newfoundland unique – from its geography and climate to its population, infrastructure, and beyond. Dive into the details:
- Geography and Size: Explore the island’s size and location.
- Climate and Weather: Weather patterns and temperature.
- Topography and Nature: Uncover the natural wonders of the island.
- Infrastructure and Travelling: Insights on reaching, staying, and making the most of your visit.
- News and Headlines: Latest News.
Geography and size of Newfoundland
Size: 108878 km²
Coastline: 12172 km
Ocean: Atlantic Ocean
Sea: Labrador Sea
Continent: North America
Newfoundland is a Colossal Island spanning 108878 km² with a coastline of 12172 km.
Archipel: –
Tectonic Plate: North America – Covers North America and parts of the Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, characterized by diverse geological features and varying levels of seismic activity.
The geographic heart of the island is pinpointed at these coordinates:
Latitude: 48.72500071 / Longitude: -56.06446798
Climate and weather of Newfoundland
Climate Zone: Continental
Climate Details: Warm-Summer Humid Continental Climate
Temperature: Warm Summer
Climate Characteristics: Features warm summers and cold winters with consistent precipitation, common in higher latitudes.
Topography and nature of Newfoundland
Timezone: UTC-03:30
Timezone places: America/St_Johns
Max. Elevation: 782 m
Mean Elevation: 215 m
Vegetation: Open Woodland
Tree Coverage: 47%
The mean elevation is 215 m. The highest elevation on the island reaches approximately 782 meters above sea level. The island is characterized by Plateau: Elevated flatlands rising sharply above the surrounding area, with a maximum elevation over 500 meters but a mean elevation less than 300 meters, forming unique highland areas on islands.
Dominating Vegetation: Open Woodland
Characterized by sparsely distributed trees with open canopy allowing sunlight to penetrate, supporting grasses and shrubs underneath. Often found in drier or transitional environments. Newfoundland has a tree cover of 47 %.
Vegetation: 15 vegetation zones – Exceptionally Diverse Island
Islands with more than ten vegetation zones are among the most ecologically rich and varied in the world. These islands are akin to miniature continents, boasting an incredible array of ecosystems. The sheer range of habitats, from high peaks to deep valleys, rainforests to deserts, creates a mosaic of life that is unparalleled. They are crucial for conservation and ecological studies.
Infrastructure and Travelling to Newfoundland
Does the island have a public airport? yes.
Newfoundland has a public and scheduled airport. The following airports are located on this island: St. Anthony Airport, Deer Lake Airport, Stephenville Airport, Gander International Airport / CFB Gander, St. John’s International Airport.
Does the island have a major port? yes.
Newfoundland is home to a major port. The following ports are situated on the island: CORNER BROOK, CLARENVILLE.
The mean population of Newfoundland is 5 per km². Newfoundland is Gently Populated. The island belongs to Canada.
The name of the island resonates across different cultures and languages. Here is how it is known around the world: Arabic: نيوفاوندلاند; German: Neufundland; Spanish: Isla de Terranova; French: Terre-Neuve; Portuguese: Terra Nova; Russian: Ньюфаундленд; Chinese: 纽芬兰岛
Continuing your journey, Sound Island is the next notable island, situated merely km away.
Canada is classified as Developed region: G7: Group of Seven – Major advanced economies, including Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The level of income is High income: OECD.
News – Latest Updates and Headlines from Newfoundland
Stay informed with the most recent news and important headlines from Newfoundland. Here’s a roundup of the latest developments.
Social Media Posts about Newfoundland
Please note: The data used here has been primarily extracted from satellite readings. Deviations from exact values may occur, particularly regarding the height of elevations and population density. Land area and coastline measurements refer to average values at mean high tide.
