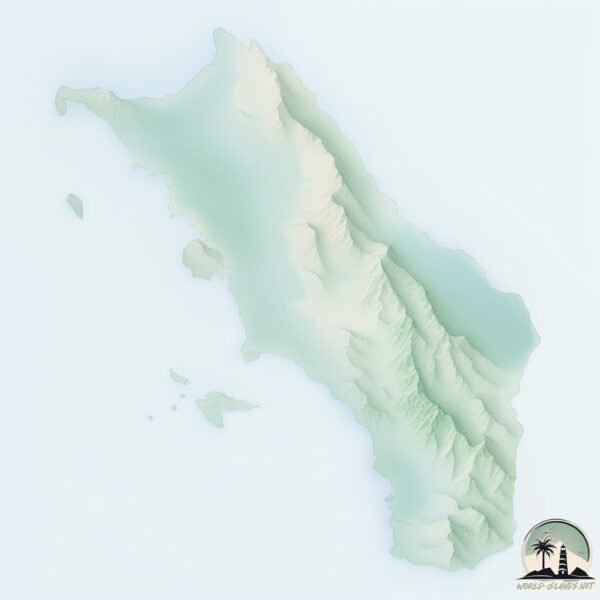
Welcome to Nias, a Tropical island in the Indian Ocean, part of the majestic Indian Ocean. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of what makes Nias unique – from its geography and climate to its population, infrastructure, and beyond. Dive into the details:
Geography and size of Nias
Size: 4150 km²
Coastline: 459 km
Ocean: Indian Ocean
Sea: Indian Ocean
Continent: Asia
Nias is a Very Large Island spanning 4150 km² with a coastline of 459 km.
Archipel: Malay Archipelago – The world’s largest archipelago, located between mainland Southeast Asia and Australia, known for its immense biodiversity and cultural diversity.
Tectonic Plate: Sunda – Extends across Southeast Asia, encompassing parts of the Sunda Shelf, known for its interaction with the Australian Plate, contributing to volcanic activity in Indonesia.
The geographic heart of the island is pinpointed at these coordinates:
Latitude: 1.06392084 / Longitude: 97.58694562
Climate and weather of Nias
Climate Zone: Tropical
Climate Details: Tropical Rainforest Climate
Temperature: Hot
Climate Characteristics: This climate is typified by heavy rainfall throughout the year, high humidity, and consistently high temperatures, leading to lush rainforests and rich biodiversity. Seasonal temperature variations are minimal.
Topography and nature of Nias
Timezone: UTC+07:00
Timezone places: Asia/Jakarta
Max. Elevation: 729 m
Mean Elevation: 132 m
Vegetation: Evergreen Broadleaf Forest
Tree Coverage: 59%
The mean elevation is 132 m. The highest elevation on the island reaches approximately 729 meters above sea level. The island is characterized by Plateau: Elevated flatlands rising sharply above the surrounding area, with a maximum elevation over 500 meters but a mean elevation less than 300 meters, forming unique highland areas on islands.
Dominating Vegetation: Evergreen Broadleaf Forest
Characterized by dense, lush canopies of broadleaf trees that retain their leaves year-round. These forests are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions and are known for their high biodiversity. Nias has a tree cover of 59 %.
Vegetation: 13 vegetation zones – Exceptionally Diverse Island
Islands with more than ten vegetation zones are among the most ecologically rich and varied in the world. These islands are akin to miniature continents, boasting an incredible array of ecosystems. The sheer range of habitats, from high peaks to deep valleys, rainforests to deserts, creates a mosaic of life that is unparalleled. They are crucial for conservation and ecological studies.
Infrastructure and Travelling to Nias
Does the island have a public airport? yes.
Nias has a public and scheduled airport. The following airports are located on this island: Binaka Airport.
Does the island have a major port? no.
There are no major ports on Nias. The closest major port is SIBOLGA, approximately 123 km away.
The mean population of Nias is 164 per km². Nias is Moderately Inhabited. The island belongs to Indonesia.
The name of the island resonates across different cultures and languages. Here is how it is known around the world: Arabic: نياس; German: Nias; Spanish: Nías; French: Nias; Portuguese: Nias; Russian: Ниас; Chinese: 尼亞斯島
Continuing your journey, Pulau Bangkaru is the next notable island, situated merely km away.
The Best Kept Secret of Indonesia | Nias island
Welcome to Nias Island, Indonesia! In this video, we explore the unique tradition of stone jumping (Fahombo), where locals leap ...The Best Kept Secret of Indonesia | Nias island
Welcome to Nias Island, Indonesia! In this video, we explore the ...
Welcome to Nias Island, Indonesia! In this video, we explore the unique tradition of stone jumping (Fahombo), where locals leap ...
Trip to Nias Island -Indonesia Travel Video- Pulau Nias-with subtitle
This video is about A trip to Nias Island on the Western Coast of ...
This video is about A trip to Nias Island on the Western Coast of North Sumatra Indonesia. The purpose of the trip is to do a survey ...
travel to nias island indonesia
nias island indonesia,Nias is an island covering an area of ??4624 ...
nias island indonesia,Nias is an island covering an area of ??4624 square kilometers located in the west of the island of Sumatra, ...
The Unique “Stone Jump” Tradition of Indonesia 🇮🇩 | Nias Island #facts #shorts #unique
On Nias Island, Indonesia, young men must leap over a 2-meter-high ...
On Nias Island, Indonesia, young men must leap over a 2-meter-high stone wall to prove they're ready for adulthood. This ancient ...
Flying from Poland to Nias Island | Episode 1
ROAD TO PARADISE! Bumpy Rides & Hidden Gems of Nias Island: A Travel Diary 2024
Join me on an unforgettable journey to Nias Island, Indonesia! From ...
Join me on an unforgettable journey to Nias Island, Indonesia! From the moment we arrived, we were greeted with a surprise ...
Bright culture - Dark history | Nias Island – Ep. 91
Headhunting was practiced on this remote island until the late 20th ...
Headhunting was practiced on this remote island until the late 20th Century! After so long sailing amongst uninhabited islands ...
Biggest Swell in 2022 - Nias - RAWFILES - 24/MAY - 4K
The first solid swell of the Season hit the Lagundri Bay heavy, lots ...
The first solid swell of the Season hit the Lagundri Bay heavy, lots of unridden double ups, specially around high-tide, perfect ...
Who made monoliths and stone tables in Nias Island of Indonesia?
Nias Island is very much unknown to the outside world. Niasans have ...
Nias Island is very much unknown to the outside world. Niasans have many megalithic mysteries that will shock the world just as ...
One of the most celebrated surf clips ever captured. Tedi at Nias, Indonesia by Balint Hambalko.
One of the most celebrated surf clips ever captured. One wave by Tedi ...
One of the most celebrated surf clips ever captured. One wave by Tedi Kurniadi at Nias, Indonesia, captured by Balint Hambalko.
Nias Island
Provided to YouTube by DistroKid Nias Island · Alexstan Project · 김태수 ...
Provided to YouTube by DistroKid Nias Island · Alexstan Project · 김태수 · 윤승식 · STAN · Alex Jung · 강재구 AnalogTone studio ...
Brief information about Nias Island in North Sumatra
Brief information about Nias Island in North Sumatra. Nias is The ...
Brief information about Nias Island in North Sumatra. Nias is The Largest of The Islands of Sumatra that are Part of North Sumatra ...
Nias - Indonesia - Surf Guide
In this short film i would like to tell you about the surfing and ...
In this short film i would like to tell you about the surfing and travelling in south Nias, western Sumatra, Indonesia. I was lucky ...
Discovering the hidden gems of Nias Island in the past | A journey through time
Do you want to take a trip back in time to the beautiful island of ...
Do you want to take a trip back in time to the beautiful island of Nias? In this captivating video, we will explore the fascinating ...
"Nias Island: A Journey Beyond the Ordinary"- Indonesia #visitindonesia #travel #tour
Welcome to Explore Indonesia! If you're looking for a travel ...
Welcome to Explore Indonesia! If you're looking for a travel destination that combines breathtaking nature, rich culture, and ...
Travel to the islands of Sumatra. Indonesia 2011. Nias Sumatra Siberut
part 1 - ...
RAW DAYS | Nias, Indonesia | Historic waves in 2018
Mind surf trip to Nias, North Sumatra, Indonesia. "RAW DAYS" is a ...
Mind surf trip to Nias, North Sumatra, Indonesia. "RAW DAYS" is a NobodySurf Original video series featuring a day in the world's ...
Surfing in Nias, welcome to Nias Island
surfing sumatra nias island accommodation and tourist information ...
surfing sumatra nias island accommodation and tourist information where legends are made when you can pull in on stand up ...
TRADISI SUKU NIAS YANG MEMUKAU MASYARAKAT INDONESIA😍❤️🇮🇩
TRADISI SUKU NIAS YANG MEMUKAU MASYARAKAT INDONESIA ❤️ #nias ...
TRADISI SUKU NIAS YANG MEMUKAU MASYARAKAT INDONESIA ❤️ #nias #hombobatu #tradisi.
Booking your room in nias island sleep well surf well #niasisland #waves #surfers #home
RAW DAYS | Nias, Indonesia | Dreamy surfing session
Mind surf trip to Nias, North Sumatra, Indonesia. "RAW DAYS" is a ...
Mind surf trip to Nias, North Sumatra, Indonesia. "RAW DAYS" is a NobodySurf Original video series featuring a day in the world's ...
Nias Island - Megalithic culture in Indonesia
This is Nias Island, located off the coast of North Sumatera in ...
This is Nias Island, located off the coast of North Sumatera in Indonesia. It is one of the last surviving megalithic cultures in the ...
Nias Culture of Nias Island Indonesia ثقافة نياس ، اندونيسيا
Nias Culture, way of life, food, history, geographical location, and more.
Nias Culture, way of life, food, history, geographical location, and more.
Spearfishing Dog Tooth Tuna in Nias Island - Indonesia
Please kindly watch our Spearfishing Trip when shooting dog tooth tuna ...
Please kindly watch our Spearfishing Trip when shooting dog tooth tuna in Nias Island - Indonesia. Nias Island is an archipelago ...
Indonesia is classified as Emerging region: MIKT: Mexico, Indonesia, South Korea, and Turkey – Economies recognized for their development potential and emerging market status. The level of income is Lower middle income.
News – Latest Updates and Headlines from Nias
Stay informed with the most recent news and important headlines from Nias. Here’s a roundup of the latest developments.
Loading...
Social Media Posts about Nias
Loading...
Please note: The data used here has been primarily extracted from satellite readings. Deviations from exact values may occur, particularly regarding the height of elevations and population density. Land area and coastline measurements refer to average values at mean high tide.