Quaker
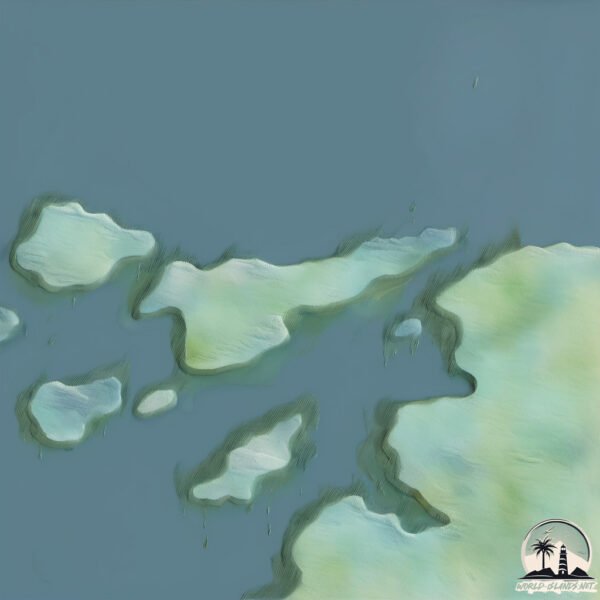
Welcome to Quaker, a Temperate island in the South Atlantic Ocean, part of the majestic Atlantic Ocean. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of what makes Quaker unique – from its geography and climate to its population, infrastructure, and beyond. Dive into the details:
- Geography and Size: Explore the island’s size and location.
- Climate and Weather: Weather patterns and temperature.
- Topography and Nature: Uncover the natural wonders of the island.
- Infrastructure and Travelling: Insights on reaching, staying, and making the most of your visit.
- News and Headlines: Latest News.
Geography and size of Quaker
Size: 2.096 km²
Coastline: 7.8 km
Ocean: Atlantic Ocean
Sea: South Atlantic Ocean
Continent: South America
Quaker is a Small Island spanning 2.1 km² with a coastline of 7.8 km.
Archipel: Falkland Islands – Located in the South Atlantic Ocean, this British Overseas Territory is known for its rugged terrain, biodiversity, and historical significance.
Tectonic Plate: South America – A major plate covering the South American continent and part of the Atlantic Ocean, known for the Andes mountain range and significant seismic and volcanic activity.
The geographic heart of the island is pinpointed at these coordinates:
Latitude: -51.78467414 / Longitude: -61.05830798
Climate and weather of Quaker
Climate Zone: Temperate
Climate Details: Subpolar Oceanic Climate
Temperature: Cold Summer
Climate Characteristics: Predominantly cold with cool summers and no dry season. Often found in coastal areas at higher latitudes or on islands.
Topography and nature of Quaker
Timezone: UTC-04:00
Timezone places: America/La_Paz
Max. Elevation: 37 m
Mean Elevation: 20 m
Vegetation: Shrubland
Tree Coverage: 93%
The mean elevation is 20 m. The highest elevation on the island reaches approximately 37 meters above sea level. The island is characterized by Plains: Flat, low-lying lands characterized by a maximum elevation of up to 200 meters. On islands, plains are typically coastal lowlands or central flat areas.
Dominating Vegetation: Shrubland
Dominated by shrubs and small bushes, these areas are typical in dry, rocky, or sandy environments, as well as in regions with poor soil fertility. Quaker has a tree cover of 93 %.
Vegetation: 6 vegetation zones – Very Highly Diverse Island
Islands in this range are ecological powerhouses, showcasing a wide array of vegetation zones. Each zone, from lush rainforests to arid scrublands, coastal mangroves to mountainous regions, contributes to a complex and interdependent ecosystem. These islands are often hotspots of biodiversity, supporting numerous species and intricate ecological processes.
Infrastructure and Travelling to Quaker
Does the island have a public airport? no.
There is no public and scheduled airport on Quaker. The nearest airport is Mount Pleasant Airport, located 288 km away.
Does the island have a major port? no.
There are no major ports on Quaker. The closest major port is STANLEY, approximately 356 km away.
The mean population of Quaker is 0 per km². Quaker is Uninhabited. The island belongs to Falkland Is..
Continuing your journey, Weddel is the next notable island, situated merely km away.
Gorillaz - Cracker Island ft. Thundercat (Official Video)



Falkland Is. is classified as Developed region: G7: Group of Seven – Major advanced economies, including Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The level of income is High income: OECD.
News – Latest Updates and Headlines from Quaker
Stay informed with the most recent news and important headlines from Quaker. Here’s a roundup of the latest developments.
Please note: The data used here has been primarily extracted from satellite readings. Deviations from exact values may occur, particularly regarding the height of elevations and population density. Land area and coastline measurements refer to average values at mean high tide.
