Welcome to Rabbit, a Temperate island in the South Atlantic Ocean, part of the majestic Atlantic Ocean. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of what makes Rabbit unique – from its geography and climate to its population, infrastructure, and beyond. Dive into the details:
Geography and size of Rabbit
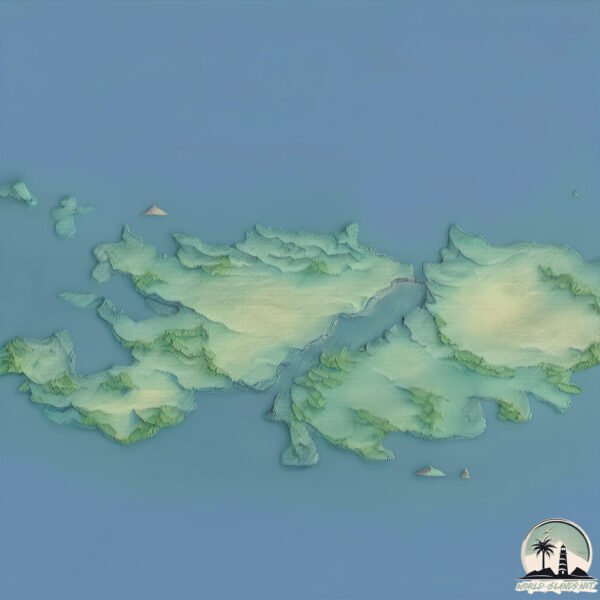
Size: 1.942 km²
Coastline: 7.8 km
Ocean: Atlantic Ocean
Sea: South Atlantic Ocean
Continent: South America
Rabbit is a Small Island spanning 1.9 km² with a coastline of 7.8 km.
Archipel: Falkland Islands – Located in the South Atlantic Ocean, this British Overseas Territory is known for its rugged terrain, biodiversity, and historical significance.
Tectonic Plate: South America – A major plate covering the South American continent and part of the Atlantic Ocean, known for the Andes mountain range and significant seismic and volcanic activity.
The geographic heart of the island is pinpointed at these coordinates:
Latitude: -51.5302219 / Longitude: -60.26652997
Climate and weather of Rabbit
Climate Zone: Temperate
Climate Details: Subpolar Oceanic Climate
Temperature: Cold Summer
Climate Characteristics: Predominantly cold with cool summers and no dry season. Often found in coastal areas at higher latitudes or on islands.
Topography and nature of Rabbit
Timezone: UTC-04:00
Timezone places: America/La_Paz
Max. Elevation: 76 m
Mean Elevation: 25 m
Vegetation: Open Woodland
Tree Coverage: 16%
The mean elevation is 25 m. The highest elevation on the island reaches approximately 76 meters above sea level. The island is characterized by Plains: Flat, low-lying lands characterized by a maximum elevation of up to 200 meters. On islands, plains are typically coastal lowlands or central flat areas.
Dominating Vegetation: Open Woodland
Characterized by sparsely distributed trees with open canopy allowing sunlight to penetrate, supporting grasses and shrubs underneath. Often found in drier or transitional environments. Rabbit has a tree cover of 16 %.
Vegetation: 5 vegetation zones – Highly Diverse Island
With five different vegetation zones, these islands offer a rich tapestry of ecosystems. The variety could include dense forests, open meadows, wetlands, coastal zones, and more. This level of diversity supports an intricate web of life, with each zone playing a vital role in the overall ecological health and balance of the island.
Infrastructure and Travelling to Rabbit
Does the island have a public airport? no.
There is no public and scheduled airport on Rabbit. The nearest airport is Mount Pleasant Airport, located 55 km away.
Does the island have a major port? no.
There are no major ports on Rabbit. The closest major port is STANLEY, approximately 125 km away.
The mean population of Rabbit is 0 per km². Rabbit is Uninhabited. The island belongs to Falkland Is..
The name of the island resonates across different cultures and languages. Here is how it is known around the world: Arabic: جزيرة فوكلاند الشرقية; German: Ostfalkland; Spanish: Isla Soledad; French: Malouine orientale; Portuguese: Malvina Oriental; Russian: Восточный Фолкленд; Chinese: 索莱达岛
Continuing your journey, Golding is the next notable island, situated merely km away.
The Mystery of Rabbit Island
Imagine an island filled only with rabbits. Okunoshima is a small island in Japan's Inland Sea. It's called "Rabbit Island" because ...The Mystery of Rabbit Island
Imagine an island filled only with rabbits. Okunoshima is a small ...
Imagine an island filled only with rabbits. Okunoshima is a small island in Japan's Inland Sea. It's called "Rabbit Island" because ...
Rabbits On Okunoshima Island Swarm Tourist
A whopping 600 rabbits! Trip to Japan's Amazing Rabbit Island🐰
Please experience a travel to Japan! I visited Rabbit Island, which is ...
Please experience a travel to Japan! I visited Rabbit Island, which is full of rabbits. A cute and friendly bunny. The hotel's ...
Exclusive Tour of Rabbit Island Japan by a Bunny Expert
Shai took a trip to Ōkunoshima, Japan, otherwise known as The Rabbit ...
Shai took a trip to Ōkunoshima, Japan, otherwise known as The Rabbit Island. You won't believe how many rabbits he met there.
Why Is This Island Filled With Rabbits?
Imagine an island filled only with rabbits. Okunoshima is a small ...
Imagine an island filled only with rabbits. Okunoshima is a small island in Japan's Inland Sea. It's called "Rabbit Island" because ...
Freddie Gibbs - Rabbit Island (Official Visualizer)
Rabbit: “May I get on your lap?”
"Okunoshima" in Takehara City, Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan. This ...
"Okunoshima" in Takehara City, Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan. This island in the Seto Inland Sea is home to over 900 rabbits, and ...
See Why They Call It "Rabbit Island" | Nat Geo Wild
The small island of Ōkunoshima in Japan has become famous for a large ...
The small island of Ōkunoshima in Japan has become famous for a large and growing population of non-native rabbits.
The moment I petted the rabbit, it demanded more!
"Okunoshima" in Takehara City, Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan. This ...
"Okunoshima" in Takehara City, Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan. This island in the Seto Inland Sea is home to over 900 rabbits, and ...
Kawaii!The Only RABBIT ISLAND in the World - Uninhabited with 700 Wild Rabbits | Japanese Island
What is Ohkunojima? An uninhabited island belonging to Takehara City, ...
What is Ohkunojima? An uninhabited island belonging to Takehara City, Hiroshima Prefecture It takes about 15 minutes by boat ...
Rabbit Island in Japan 🇯🇵🏝🐰
The Only Bunny Island in the World 🏝️🐇 Visiting Japan’s Rabbit Paradise ✨
I visited Ōkunoshima in Hiroshima Prefecture. Ōkunoshima is the only ...
I visited Ōkunoshima in Hiroshima Prefecture. Ōkunoshima is the only island in the world where wild rabbits live. I was able to ...
BUNNY ISLAND : The fluffiest paradise in the world. 🐇
BUNNY ISLAND : The fluffiest paradise in the world. Bunny Island ...
BUNNY ISLAND : The fluffiest paradise in the world. Bunny Island actually exists! Sounds like a dream! Right? But it really ...
Rabbit: "What the heck is that sound?"
"Okunoshima" in Takehara City, Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan. This ...
"Okunoshima" in Takehara City, Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan. This island in the Seto Inland Sea is home to over 900 rabbits, and ...
Why is this island chock full of rabbits? 🐇🐇🐇 - BBC
The Dark, Twisted Truth About Rabbit Island Japan
Follow me on my journey to rabbit island, also known as Okunoshima in ...
Follow me on my journey to rabbit island, also known as Okunoshima in Japan. Here, I discover that not everything is as cute as it ...
Kerem Gell - Rabbit Island
Japan's RABBIT ISLAND - Incredible!
In this Rabbit Island pilot video, we visit Ōkunoshima (大久野島), a small ...
In this Rabbit Island pilot video, we visit Ōkunoshima (大久野島), a small island located in the Inland Sea of Japan in the city of ...
I petted the rabbit and it melted.
"Okunoshima" in Takehara City, Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan. This ...
"Okunoshima" in Takehara City, Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan. This island in the Seto Inland Sea is home to over 900 rabbits, and ...
[Rabbit Island, JAPAN] 600 rabbits live on Rabbit Island travel🐰🥕 Cute rabbit paradise! | 大久野島 うさぎ島
We visited “Rabbit Island,” the only rabbit paradise in the world. ...
We visited “Rabbit Island,” the only rabbit paradise in the world. (Okunoshima / Tadanoumi-cho, Takehara City, Hiroshima ...
Exploring Japan's Adorable Rabbit Island 🐰🌴 | Ōkunoshima
Inside Japan's Rabbit Island 🐰
I visited Japan's famous Rabbit Island, also known as Okunoshima, ...
I visited Japan's famous Rabbit Island, also known as Okunoshima, where hundreds of wild rabbits roam freely across the island.
[Rabbit Island, JAPAN] Cute baby rabbits in paradise🐰 Island of 600 wild bunnies🐇 | Okunoshima 大久野島
We visited the world's only rabbit paradise, "Rabbit Island" ...
We visited the world's only rabbit paradise, "Rabbit Island" (Okunoshima - Tadanoumi-cho, Takehara City, Hiroshima Prefecture).
History behind "Rabbit Island"
History behind "Rabbit Island"
History behind "Rabbit Island"
I petted a baby rabbit's butt and it melted.
"Okunoshima" in Takehara City, Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan. This ...
"Okunoshima" in Takehara City, Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan. This island in the Seto Inland Sea is home to over 900 rabbits, and ...
Falkland Is. is classified as Developed region: G7: Group of Seven – Major advanced economies, including Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The level of income is High income: OECD.
News – Latest Updates and Headlines from Rabbit
Stay informed with the most recent news and important headlines from Rabbit. Here’s a roundup of the latest developments.
Loading...
Please note: The data used here has been primarily extracted from satellite readings. Deviations from exact values may occur, particularly regarding the height of elevations and population density. Land area and coastline measurements refer to average values at mean high tide.



















![[Rabbit Island, JAPAN] 600 rabbits live on Rabbit Island travel🐰🥕 Cute rabbit paradise! | 大久野島 うさぎ島](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/6Z_-j-qb7XM/mqdefault.jpg)


![[Rabbit Island, JAPAN] Cute baby rabbits in paradise🐰 Island of 600 wild bunnies🐇 | Okunoshima 大久野島](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/mQDmkgDE1_c/mqdefault.jpg)


