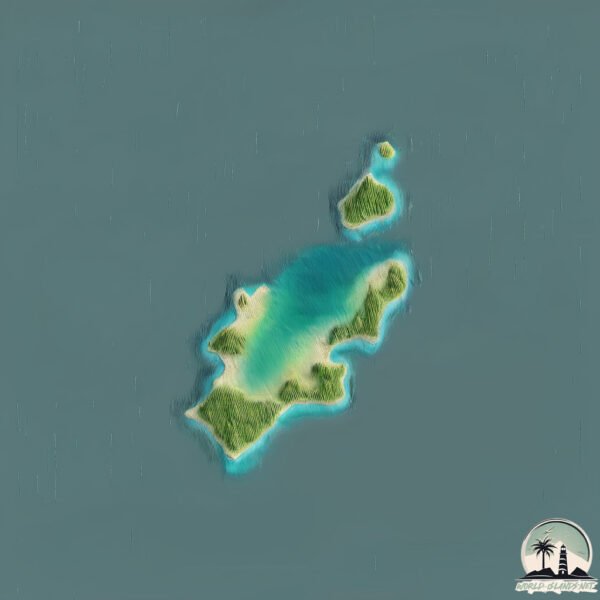
Welcome to St. Paul Island, a Continental island in the Gulf of St. Lawrence, part of the majestic Atlantic Ocean. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of what makes St. Paul Island unique – from its geography and climate to its population, infrastructure, and beyond. Dive into the details:
Geography and size of St. Paul Island
Size: 4.999 km²
Coastline: 16.7 km
Ocean: Atlantic Ocean
Sea: Gulf of St. Lawrence
Continent: North America
St. Paul Island is a Small Island spanning 5 km² with a coastline of 16.7 km.
Archipel: –
Tectonic Plate: North America – Covers North America and parts of the Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, characterized by diverse geological features and varying levels of seismic activity.
The geographic heart of the island is pinpointed at these coordinates:
Latitude: 47.20209268 / Longitude: -60.15121879
Climate and weather of St. Paul Island
Climate Zone: Continental
Climate Details: Subarctic Climate
Temperature: Cold Summer
Climate Characteristics: Characterized by long, extremely cold winters and short, cool summers, often found in northern latitudes of North America and Eurasia.
Topography and nature of St. Paul Island
Timezone: UTC-04:00
Timezone places: America/La_Paz
Max. Elevation: 93 m
Mean Elevation: 46 m
Vegetation: Deciduous Needleleaf Forest
Tree Coverage: 87%
The mean elevation is 46 m. The highest elevation on the island reaches approximately 93 meters above sea level. The island is characterized by Plains: Flat, low-lying lands characterized by a maximum elevation of up to 200 meters. On islands, plains are typically coastal lowlands or central flat areas.
Dominating Vegetation: Deciduous Needleleaf Forest
Consists of needleleaf trees that shed their needles annually. This type of forest is less common and can be found in certain cold, northern regions. St. Paul Island has a tree cover of 87 %.
Vegetation: 4 vegetation zones – Diverse Island
Four distinct vegetation zones mark these islands as ecologically diverse. They might feature varied landscapes such as forests, beaches, grasslands, and rocky areas. Such diversity reflects the island’s complex ecological interactions and varied habitats, which can support a rich array of wildlife and plant species.
Infrastructure and Travelling to St. Paul Island
Does the island have a public airport? no.
There is no public and scheduled airport on St. Paul Island. The nearest airport is Sydney / J.A. Douglas McCurdy Airport, located 114 km away.
Does the island have a major port? no.
There are no major ports on St. Paul Island. The closest major port is LITTLE BRAS D OR, approximately 105 km away.
The mean population of St. Paul Island is 0 per km². St. Paul Island is Uninhabited. The island belongs to Canada.
Continuing your journey, Cape Breton is the next notable island, situated merely km away.
St. Paul Island store run
This is a basic tutorial on social distancing store run etiquette video for community members. Brough to you by the City and Tribal ...St. Paul Island store run
This is a basic tutorial on social distancing store run etiquette ...
This is a basic tutorial on social distancing store run etiquette video for community members. Brough to you by the City and Tribal ...
Town of St. Paul, Alaska | Remote Alaska
One of the most remote settlements in all of Alaska, the village of ...
One of the most remote settlements in all of Alaska, the village of St. Paul stands alone amid the vast Bering Sea, a place where ...
St Paul & Amsterdam
je vous presente L'ile de St Paul & Amsterdam petite mission dans les ...
je vous presente L'ile de St Paul & Amsterdam petite mission dans les taaf septembre 2020.
st paul island ns kayaking adventures.
kayaking rough waters to st paul island ns from cape north ns.this ...
kayaking rough waters to st paul island ns from cape north ns.this video is st paul island ns lighthouse adventure[part 1 going up ...
I Spent a Week on St Paul Island and Found the MOST UNEXPECTED Gem!
travel #explore #alaska Join me on an unforgettable adventure to St. ...
travel #explore #alaska Join me on an unforgettable adventure to St. Paul Island, Alaska, a remote treasure of the Bering Sea!
Discovering St. Paul Island: A Hidden Gem in Alaska
Join us as we embark on an unforgettable journey to St. Paul Island, a ...
Join us as we embark on an unforgettable journey to St. Paul Island, a hidden gem nestled in the breathtaking wilderness of ...
The Forgotten Castaway of St. Paul Island
Stranded in the North Atlantic, one man defied nature and fate. ...
Stranded in the North Atlantic, one man defied nature and fate. Discover the gripping survival tale of the St. Paul castaway!
îld saint paul island in indian ocean #asia #indianocean #ocean #map #googleearth #beach#oceanatlas
New Spots to Stay in Cape Breton & Visiting St. Paul Island with Nothern Tip Charters | Nova Scotia
Join us as we explore with Cape Breton Northern Tip Charters on an ...
Join us as we explore with Cape Breton Northern Tip Charters on an exciting adventure to St. Paul Island in Nova Scotia while ...
St. Paul Island, in 4K
I had the privilege of visiting St. Paul, AK for work recently and ...
I had the privilege of visiting St. Paul, AK for work recently and thought it would be a great place to capture on my drone, being that ...
King Eider Outfitters ST Paul Island Aerial tour
Hunt with Alaska's Premier King Eider Outfitter on St Paul Island, ...
Hunt with Alaska's Premier King Eider Outfitter on St Paul Island, Aleutian Island Waterfowlers full time since 2001.
St Paul Island, Nova Scotia
From 2000' April 5th 2023 in Cessna 150.
From 2000' April 5th 2023 in Cessna 150.
St Paul's Islands in Malta
valletta #jet2holidays #localnews #malta #maltajobsforindian walk ...
valletta #jet2holidays #localnews #malta #maltajobsforindian walk around St Paul's Islands.
The Island of ST pauls The last frontier
St. Pauls Island part of the Pribilof Islands Alaska at the Bering ...
St. Pauls Island part of the Pribilof Islands Alaska at the Bering sea. Birders walhalla. photographic top location. Eric Rock and ...
St Paul’s Shipwreck- #StPaulsShipwreck #StPaulsIsland #Selmunett #Mellieha #MaltaHistory
MaltaHeritage #StPaulsStory #HistoricalMalta #MaltaLandmarks ...
MaltaHeritage #StPaulsStory #HistoricalMalta #MaltaLandmarks #BiblicalEvents #StPaulsLegacy #MaltaShipwreck ...
Vlass - St. Paul Island, Alaska
Aleutian Pribilof Islands Association - Dietary Risks and Benefits ...
Aleutian Pribilof Islands Association - Dietary Risks and Benefits Project - 2004 -
http://www.apiai.com/St'Pauls Islands Malta in 4k
St Paul's Island (Maltese: Il-Gżejjer ta' San Pawl), also known as ...
St Paul's Island (Maltese: Il-Gżejjer ta' San Pawl), also known as Selmunett, is a small island off Selmun near the north-east of the ...
Stranded at a Lobster Factory and Left to Die…
Seven people were left on this desolate, remote island with little ...
Seven people were left on this desolate, remote island with little food to guard a lobster factory over the winter. They were only ...
Tying up at St. Paul Island 2015
Saint Paul, l'île extraterrestre
Perdu au Sud de l'océan indien, le cratère à demi immergé de l'île ...
Perdu au Sud de l'océan indien, le cratère à demi immergé de l'île secrète de Saint Paul. Survol exceptionnel en hélico.
Chopper landing at St. Paul's Island, Nova Scotia
From pilot's view, EC 120B chopper conducts flyover and landing at ...
From pilot's view, EC 120B chopper conducts flyover and landing at uninhabited St. Paul's Island, 20 miles north of Cape Breton, ...
Mysteries of St. Paul Island
Explore St. Paul Island's unique landscape, rare flora, and historical ...
Explore St. Paul Island's unique landscape, rare flora, and historical survival techniques used by ocean tribes. Delve into ancient ...
Alaska Travel St Paul Island
A brief Travel video to help our guest's plan for there duck hunting ...
A brief Travel video to help our guest's plan for there duck hunting trip to St PAul island with Penn Air along with hotel ...
Canada is classified as Developed region: G7: Group of Seven – Major advanced economies, including Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The level of income is High income: OECD.
News – Latest Updates and Headlines from St. Paul Island
Stay informed with the most recent news and important headlines from St. Paul Island. Here’s a roundup of the latest developments.
Loading...
Please note: The data used here has been primarily extracted from satellite readings. Deviations from exact values may occur, particularly regarding the height of elevations and population density. Land area and coastline measurements refer to average values at mean high tide.