Welcome to Vulcan, a Tropical island in the Indian Ocean, part of the majestic Indian Ocean. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of what makes Vulcan unique – from its geography and climate to its population, infrastructure, and beyond. Dive into the details:
Geography and size of Vulcan
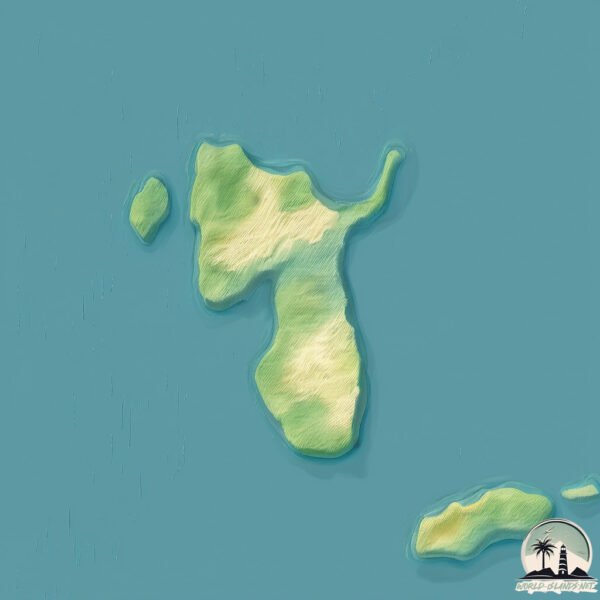
Size: 2.261 km²
Coastline: 10.6 km
Ocean: Indian Ocean
Sea: Indian Ocean
Continent: Oceania
Vulcan is a Small Island spanning 2.3 km² with a coastline of 10.6 km.
Archipel: Bonaparte Archipelago – A group of islands in northern Australia, known for their stunning natural beauty, rich indigenous history, and diverse ecosystems.
Tectonic Plate: Australia – A major tectonic plate covering Australia, New Zealand, and parts of the Indian and Pacific Oceans, known for its relative stability and occasional seismic activity.
The geographic heart of the island is pinpointed at these coordinates:
Latitude: -15.23843141 / Longitude: 124.39149324
Climate and weather of Vulcan
Climate Zone: Tropical
Climate Details: Tropical Savanna, Wet
Temperature: Hot
Climate Characteristics: Defined by distinct wet and dry seasons with high temperatures year-round. Pronounced rainfall occurs during the wet season, while the dry season is marked by drought.
Topography and nature of Vulcan
Timezone: UTC+08:00
Timezone places: Australia/Perth
Max. Elevation: 35 m
Mean Elevation: 20 m
Vegetation: Open Woodland
Tree Coverage: 79%
The mean elevation is 20 m. The highest elevation on the island reaches approximately 35 meters above sea level. The island is characterized by Plains: Flat, low-lying lands characterized by a maximum elevation of up to 200 meters. On islands, plains are typically coastal lowlands or central flat areas.
Dominating Vegetation: Open Woodland
Characterized by sparsely distributed trees with open canopy allowing sunlight to penetrate, supporting grasses and shrubs underneath. Often found in drier or transitional environments. Vulcan has a tree cover of 79 %.
Vegetation: 6 vegetation zones – Very Highly Diverse Island
Islands in this range are ecological powerhouses, showcasing a wide array of vegetation zones. Each zone, from lush rainforests to arid scrublands, coastal mangroves to mountainous regions, contributes to a complex and interdependent ecosystem. These islands are often hotspots of biodiversity, supporting numerous species and intricate ecological processes.
Infrastructure and Travelling to Vulcan
Does the island have a public airport? no.
There is no public and scheduled airport on Vulcan. The nearest airport is Broome International Airport, located 384 km away.
Does the island have a major port? no.
There are no major ports on Vulcan. The closest major port is BROOME, approximately 385 km away.
The mean population of Vulcan is 0 per km². Vulcan is Uninhabited. The island belongs to Australia.
Continuing your journey, Jungulu is the next notable island, situated merely km away.
Volcano Odyssey: Birth of an island
The Strangest Places on Earth
These are the Strangest Places on Earth! In this video, we go over ...
These are the Strangest Places on Earth! In this video, we go over strange places such as the Vulcan Point, Australia's Pink Lake, ...
Discovering the Unseen: Nature's Unimaginable Island-Ception Secrets
Join us as we explore the mind-boggling island-ception phenomenon in ...
Join us as we explore the mind-boggling island-ception phenomenon in the Philippines, where Vulcan Point Island rests within a ...
Nature’s Most Bizarre Creation (Philippines’ Taal Volcano - Vulcan Point) #facts #geography
Taal Volcano in the Philippines is one of the most unique volcanic ...
Taal Volcano in the Philippines is one of the most unique volcanic formations on Earth! Located on the island of Luzon, this ...
The Abandoned Volcanic Island Where 10,000 People Vanished (Inside a Real Ghost City) Documentary
Join us on an unforgettable journey to Montserrat, the "Pompeii of the ...
Join us on an unforgettable journey to Montserrat, the "Pompeii of the Caribbean," where we document the haunting aftermath ...
Taal Volcano Drone Video - Will Vulcan Point Survive the 2020 Eruption?
Vulcan Point is the largest island on a lake on an island on a lake on ...
Vulcan Point is the largest island on a lake on an island on a lake on an island in the world. On January 12, 2020, the volcano ...
Iceland volcano eruption offers "most beautiful" lava show
Scientists descended on the area near an erupting volcano in Iceland's ...
Scientists descended on the area near an erupting volcano in Iceland's southwest on Sunday, as lava continued to pour from the ...
Vulkan in Island: Drohne stürzt in Lavastrom
Ein Flug am aktiven Vulkan Fagradalsfjall in Island endete in einem ...
Ein Flug am aktiven Vulkan Fagradalsfjall in Island endete in einem Absturz - aber die Bilder sind spektakulär. © REUTERS Link ...
Vulcan Point is an island on a crater lake which is on Tall Volcano Island
Interesting places #unusual places.
Interesting places #unusual places.
Exploring the Coolest Recursive Island in the Philippines on Google Maps… Vulcan Point
Today, I talk about Vulcan point, part of Lake Taal and Luzon in the ...
Today, I talk about Vulcan point, part of Lake Taal and Luzon in the beautiful country of the Philippines. I discuss the volcanic ...
How Islands Are Formed by Nature | The Incredible Volcanic Process
Have you ever wondered how islands like Hawaii and the Galápagos were ...
Have you ever wondered how islands like Hawaii and the Galápagos were formed? Join us as we explore the fascinating natural ...
VULCAN POINT: A VOLCANO ISLAND LIKE NO OTHER - Part 4 [ Lost and found : Journeyman ]
This final part of the series shows a never-before-seen look into the ...
This final part of the series shows a never-before-seen look into the forbidden island of Vulcan Point---"An Island within a Lake on ...
Vulcan Point: Island-in-a-Lake-in-an-Island | Philippines’ Weirdest Geography
Vulcan Point is a rare “geography puzzle” in the Philippines. It sits ...
Vulcan Point is a rare “geography puzzle” in the Philippines. It sits inside Main Crater Lake, which is inside Taal Volcano.
The Philippines Has an Island Inside a Volcano?!
Did you know there's an island… in a lake… inside a volcano… that's in ...
Did you know there's an island… in a lake… inside a volcano… that's in a lake… inside a bigger volcano... on an island in the ...
Minecraft: Volcano Island - Build Timelapse #minecraft
Download the volcano: ...
Mind Blowing Places | Vulcan Point Philippines
Mind blowing Places | Vulcan Point Philippines. Get ready to be amazed ...
Mind blowing Places | Vulcan Point Philippines. Get ready to be amazed because we're taking you to the Philippines to explore a ...
TOP 5 Biggest Volcanoes In The World 2023 | Amazing World Facts
STUNNING Drone Video of ICELAND VOLCANO Eruption | 4K DJI FPV
The ongoing eruption of the Icelandic Volcano Fagradalsfjall in the ...
The ongoing eruption of the Icelandic Volcano Fagradalsfjall in the Geldingadalir valley was one of the most magnificent sights I ...
This Is The Ultimate Island-Ception 🔥 #shorts #canada #philippines #maps #geography #facts #funfacts
shorts #canada #philippines #island #islandception #facts ...
shorts #canada #philippines #island #islandception #facts #amazingfacts #funfacts #geography #maps #nature #interestingfacts ...
Discover Vulcan Point The World’s Largest Volcano Crater Lake
Vulcan Point, located within the Taal Volcano in the Philippines, is ...
Vulcan Point, located within the Taal Volcano in the Philippines, is the world's largest island situated within a lake on an island in ...
[Dysmantle] All Myth Tablets Locations - How to get into Vulcan Island !!!
This videos will show you all Myth Tablets that you can found in game. ...
This videos will show you all Myth Tablets that you can found in game. After completing all of them, you will open the way to a ...
MindBlowing Islandception Exploring Vulcan Point A Hidden Wonder
Embark on a mind-blowing journey to explore some of the strangest ...
Embark on a mind-blowing journey to explore some of the strangest places on Earth, including Australia's strange pink lake, ...
Lanzarote, the island carved between volcanoes and beaches - Spain
42% os the surface of Lanzarote is protected. Are you coming? ...
42% os the surface of Lanzarote is protected. Are you coming? #visitspain #spain #lanzarote #islascanarias #shorts ...
Watch a new volcanic island erupt
An erupting volcano in Iceland could be the start of decades of activity in the area
Australia is classified as Developed region: nonG7: Developed economies outside of the Group of Seven, characterized by high income and advanced economic structures. The level of income is High income: OECD.
News – Latest Updates and Headlines from Vulcan
Stay informed with the most recent news and important headlines from Vulcan. Here’s a roundup of the latest developments.
Loading...
Please note: The data used here has been primarily extracted from satellite readings. Deviations from exact values may occur, particularly regarding the height of elevations and population density. Land area and coastline measurements refer to average values at mean high tide.











![VULCAN POINT: A VOLCANO ISLAND LIKE NO OTHER - Part 4 [ Lost and found : Journeyman ]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/gdwzITsSvjM/mqdefault.jpg)








![[Dysmantle] All Myth Tablets Locations - How to get into Vulcan Island !!!](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/GjRfctOLOvI/mqdefault.jpg)




